The emergence of live TV streaming services has become a game-changer in the entertainment business. The significance of these services surpasses mere convenience, offering a host of benefits that are reshaping the way we consume television.
Live TV streaming services liberate viewers from the constraints of traditional cable subscriptions. With the ability to access live content on a variety of devices—ranging from smart TVs and laptops to smartphones and tablets—users enjoy unparalleled flexibility. This blog aims to be your go-to resource for unlocking the full potential of live TV streaming.
What is Live TV Streaming?
Live TV streaming refers to the delivery of television content over the internet in real-time, allowing viewers to watch TV channels on their devices without the need for traditional cable or satellite subscriptions. This method of content delivery has become increasingly popular due to its convenience, flexibility, and often lower cost compared to traditional cable or satellite services.
Content owners can make their live TV streams accessible across a variety of devices and platforms, catering to the preferences and habits of modern consumers. This includes apps for smart TVs, mobile devices, web browsers, and other streaming devices.
Live TV streaming platforms often incorporate interactive features, such as live chat, social media integration, and audience participation elements. This fosters engagement and allows viewers to interact with both the content and other viewers in real-time.
How do Live TV Streaming Services Work?
Content Acquisition and Licensing:
- Content Partnerships: Streaming services enter into agreements with content providers, including television networks, studios, and independent producers, to obtain the rights to stream their content.
- Licensing Agreements: These agreements outline the terms, duration, and territorial restrictions for streaming specific content. Licensing fees may vary based on factors such as viewership and exclusivity.
Infrastructure and Technology:
- Server Infrastructure: Streaming services require robust server infrastructure to handle the delivery of live content to a potentially large audience. This involves servers strategically distributed to reduce latency and improve the overall streaming experience.
- Content Delivery Networks (CDN): Live Streaming CDNs are used to distribute the load of delivering content, ensuring faster and more reliable streaming by caching content on servers located closer to the end-users.
- Streaming Protocols: Services use streaming protocols like HTTP Live Streaming (HLS) or Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP (DASH) to deliver video content efficiently, adjusting quality based on the viewer’s internet speed.
Content Ingestion and Encoding:
- Content Ingestion: This involves the process of receiving and preparing content for streaming. Content may come in various formats and resolutions, and it needs to be ingested into the streaming platform.
- Video Encoding: With live streaming encoder, content is typically encoded into different bitrates and resolutions to accommodate viewers with varying internet speeds and device capabilities. Adaptive bitrate streaming allows the service to automatically adjust the quality based on the viewer’s connection.
User Interface and Experience:
- User Interface Design: Streaming services invest in creating user-friendly interfaces accessible on various devices, including smart TVs, computers, and mobile devices.
- Personalization: Services often use algorithms to analyze user preferences and viewing history to provide personalized recommendations and content discovery features.
- Interactive Features: Some services incorporate interactive elements, such as live chat, polls, or social media integration, to enhance the user experience during live events.
Subscription and Monetization:
- Subscription Models: Services typically offer subscription plans with different pricing tiers, providing varying levels of access to content, streaming quality, and features.
- Ad-Based Models: Some services offer free access with advertisements, generating revenue through ad impressions. Premium subscribers may have an ad-free experience.
- Pay-Per-View: In addition to subscriptions, some services offer pay-per-view options for special events or premium content.
Geo-Restrictions and Rights Management:
- Geo-Restrictions: Content rights often come with geographical restrictions, and streaming services implement technologies to enforce these restrictions, ensuring content is only accessible in authorized regions.
- Rights Management: Services need to manage and track content rights to prevent unauthorized distribution or usage, enforcing contractual agreements with content providers.
Marketing and Promotion:
- Promotional Campaigns: Streaming services engage in marketing campaigns to promote their platform and exclusive content, utilizing social media, traditional advertising, and partnerships.
- Content Trailers and Teasers: Pre-release promotional materials, such as trailers and teasers, generate interest and anticipation for upcoming content.
- Partnerships: Collaborations with other companies, influencers, or platforms can help increase visibility and attract new subscribers.
Technology Behind Live TV Streaming
A. Content Delivery Networks (CDNs):
Content Delivery Networks play a crucial role in live TV streaming by optimizing the delivery of content to end-users. CDNs consist of a network of servers strategically distributed across various geographical locations. The primary purpose of CDNs in live TV streaming is to reduce latency and improve the overall performance of content delivery. Here’s how CDNs work:
- Server Distribution: CDNs have servers located in different regions to bring content physically closer to end-users. This minimizes the distance data must travel, reducing latency and improving streaming speed.
- Caching: CDNs store copies of the content in multiple servers worldwide. When a user requests a particular piece of content, the CDN delivers it from the server that is geographically closest to the user. This reduces the load on the origin server and speeds up content delivery.
- Load Balancing: CDNs employ load balancing techniques to distribute the incoming traffic efficiently across multiple servers. This ensures that no single server is overwhelmed, leading to a more stable and reliable streaming experience.
B. Adaptive Bitrate Streaming (ABR):
Adaptive Bitrate Streaming is a technique used to optimize video playback by adjusting the quality of the video in real-time based on the viewer’s network conditions. This ensures a smooth viewing experience even in the face of varying internet speeds. Here’s how ABR works:
- Multiple Bitrate Versions: The video content is encoded at multiple quality levels (different bitrates) before being delivered to the CDN. These versions are then made available for streaming.
- Dynamic Quality Adjustment: The streaming client continuously monitors the viewer’s network conditions. If the network speed is high, the client automatically selects a higher bitrate for better video quality. Conversely, if the network conditions degrade, it switches to a lower bitrate to prevent buffering and maintain a continuous stream.
- Segments and Chunking: Videos are divided into small segments or chunks. The streaming client can switch between different bitrate versions at the beginning of each segment, allowing for seamless transitions between quality levels.
C. Server Infrastructure:
The server infrastructure is the backbone of live TV streaming, encompassing various components such as:
- Origin Servers: These servers host the original content and are responsible for encoding, storing, and managing the distribution of the live stream. CDNs pull content from these origin servers.
- Media Servers: These servers handle the distribution of the live stream to end-users. They work in conjunction with CDNs to ensure efficient content delivery.
- Transcoding Servers: Transcoding is the process of converting video content into different formats and bitrates. Transcoding servers are responsible for adapting the video stream to the various quality levels required for ABR.
- Database Servers: These servers store metadata, user preferences, and other relevant information. They play a crucial role in managing user accounts, preferences, and delivering personalized content.
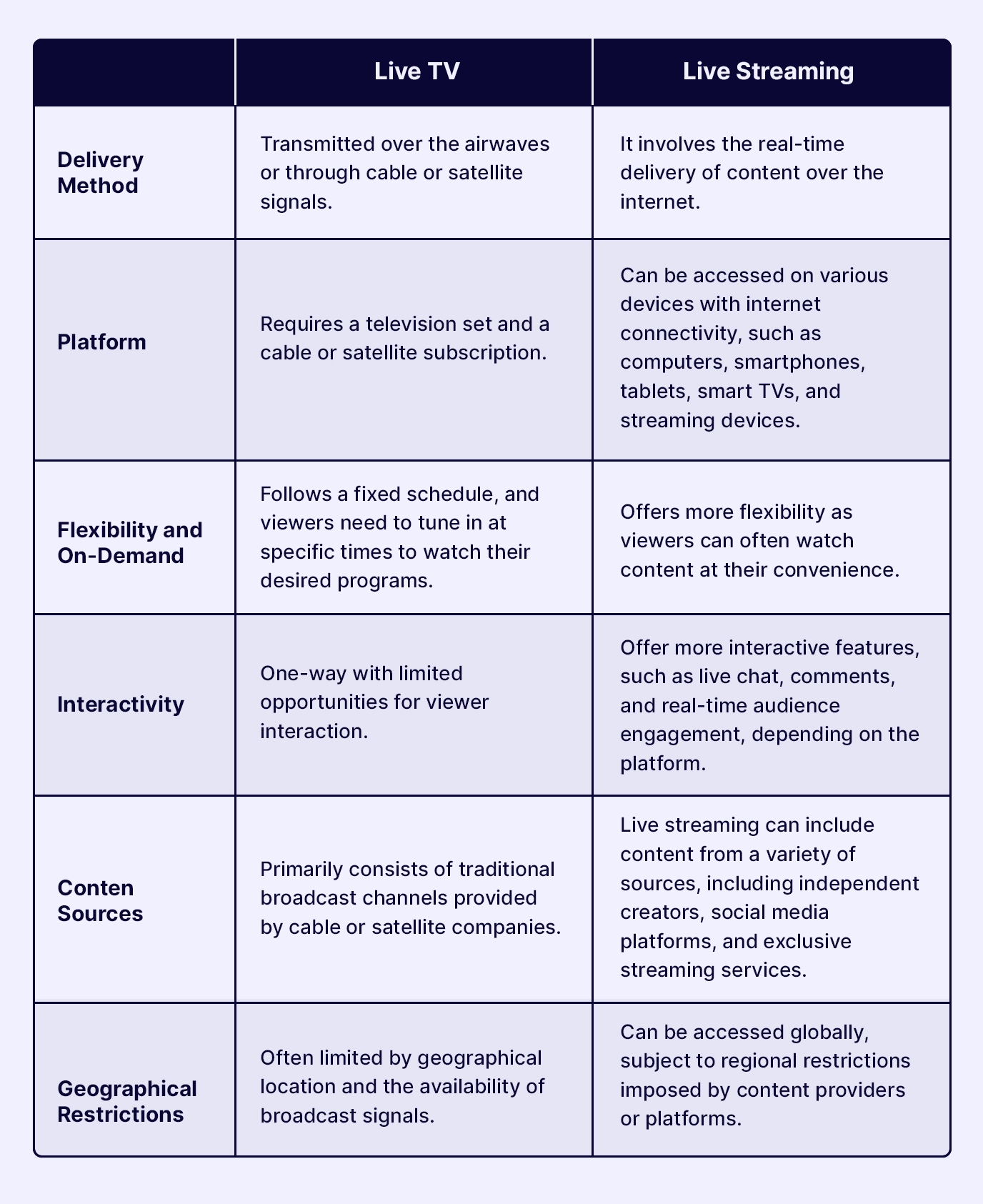
What is the Difference Between Live TV and Live Streaming?
What are the Advantages of Live TV Streaming?
Global Reach:
Live TV streaming allows content to be accessed globally, breaking down geographical barriers. This is especially beneficial for content creators and broadcasters looking to reach a diverse and international audience.
Cost Efficiency:
Compared to traditional cable or satellite TV, live TV streaming often offers cost-effective solutions. Consumers can choose from various streaming packages, eliminating the need for expensive hardware and installation fees associated with traditional TV services.
Flexibility and Scalability:
Live TV streaming services typically provide flexible subscription options, allowing users to choose plans based on their preferences. Additionally, these services are scalable, meaning users can easily upgrade or downgrade their plans based on their changing needs.
Interactivity and Engagement:
Many live TV streaming platforms offer interactive features such as live chat, polls, and social media integration. This enhances viewer engagement by allowing real-time interaction with content, fostering a sense of community among viewers.
Personalization:
Live TV streaming services often utilize algorithms to analyze user preferences and viewing habits. This data is then used to offer personalized content recommendations, enhancing the overall user experience, and making it more tailored to individual preferences.
Analytics:
Streaming services gather extensive data on user behavior, including viewing habits, preferences, and engagement metrics. This data is valuable for content providers to make informed decisions about programming, advertising, and user experience improvements.
Monetization Opportunities:
Live TV streaming provides various monetization avenues, including subscription models, pay-per-view events, and targeted advertising. This flexibility allows content creators to choose the revenue model that best suits their content and audience.
Cross-Platform Accessibility:
Viewers can access live TV streaming services on a variety of devices, including smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, and computers. This cross-platform accessibility ensures that users can enjoy content wherever and whenever they want.
Content Discovery and Recommendations:
Live TV streaming platforms often employ advanced recommendation algorithms to suggest relevant content based on a user’s viewing history and preferences. This helps users discover new content that aligns with their interests.
Adaptation to Changing Consumer Habits:
As consumer habits evolve, live TV streaming services can quickly adapt to new technologies and trends. This adaptability ensures that these services remain relevant and attractive to a wide range of audiences.
Conclusion
Live TV streaming services have revolutionized the way we consume television content, offering unparalleled flexibility and convenience.
Live TV streaming services have not only changed how we watch television but have empowered viewers to tailor their entertainment experience to suit their individual preferences.
Muvi Live allows you to live stream TV programs and any other events, shows, tournaments on any device instantly and help keep viewers engaged with DVR, live chat, and video cards. Our all-in-one DRM-enabled live streaming platform provides a secure environment for your live streams. Start for free now!

















Add your comment