In the rapidly evolving world of streaming businesses, staying ahead of the technological curve is crucial for delivering high-quality video content efficiently. One such technological advancement that has revolutionized the streaming industry is the H.265 codec.
Also known as High-Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), H.265 is the successor to its predecessor, H.264, offering superior compression capabilities and improved video quality. With its ability to significantly reduce bandwidth requirements while maintaining excellent visual fidelity, the H.265 codec has become a game-changer for streaming platforms, content creators, and viewers alike.
As streaming services continue to experience explosive growth, the demand for efficient video compression solutions has never been greater. The H.265 codec addresses this need by utilizing advanced compression algorithms to reduce the file size of video content without compromising its quality.
By efficiently encoding and decoding videos, H.265 enables streaming platforms to deliver high-definition content seamlessly, even under limited bandwidth conditions. But there’s more. Let’s know all as we delve deeper.
What Is a Video Codec?
A video codec, short for “compression-decompression,” is a software or hardware algorithm used to compress and decompress digital video data. It is a crucial component in the process of storing, transmitting, and playing back video files efficiently.
Video codecs employ various compression techniques to reduce the size of video files without significant loss of quality. They achieve this by eliminating redundant or irrelevant information from the video data, taking advantage of the inherent redundancies and limitations of human perception.
During compression, a video codec analyzes the video frames, identifies patterns, and encodes the data using compression algorithms. The compressed video data can then be stored or transmitted more efficiently.
On the decoding side, the video codec reverses the compression process. It receives the compressed video data and decodes it, reconstructing the original video frames for playback. The decoding process involves decompressing the data and applying inverse operations to restore the video to its original quality.
There are various video codecs available, each employing different compression algorithms and techniques. Popular video codecs include H.264, H.265 (HEVC), VP9, AV1, and MPEG-4. These codecs have different levels of compression efficiency, quality, and compatibility with different devices and platforms.
H.265 Codec – An Overview
H.265, also known as High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), is a video compression standard that offers significant advancements over its predecessors. It is designed to provide higher compression efficiency and improved video quality compared to previous codecs like H.264.
The H.265 codec utilizes advanced compression algorithms to reduce the file size of video content while maintaining excellent visual fidelity. By analyzing the video frames and efficiently encoding the data, H.265 achieves a higher compression ratio, resulting in smaller file sizes without compromising the quality of the video.
This compression efficiency is particularly valuable for streaming platforms, as it allows for the delivery of high-quality video content while optimizing bandwidth usage.
The Key Benefits of Using H.265 Codec
Now let’s explore five key benefits of using the H.265 codec.
1. Superior Compression Efficiency
One of the primary benefits of the H.265 codec is its remarkable compression efficiency. It utilizes advanced algorithms and techniques to significantly reduce the file size of video content while maintaining high-quality visuals.
Compared to its predecessor H.264, H.265 can achieve up to 50% more compression, resulting in smaller file sizes without sacrificing video quality. This compression efficiency offers several advantages, including reduced bandwidth requirements, improved storage utilization, and faster transmission speeds.
2. Enhanced Video Quality
Despite achieving higher compression, the H.265 codec retains exceptional video quality. It supports various video resolutions, including 4K and even 8K, delivering stunning visuals with greater detail, clarity, and color accuracy.
Furthermore, H.265 provides enhanced support for advanced video features such as High Dynamic Range (HDR) and wider color gamut, allowing for more vibrant and lifelike imagery. This improved video quality enhances the overall viewing experience, providing users with immersive and visually captivating content.
In contrast to H.264’s macroblocks, H.265 employs Coding Tree Units (CTUs) to process information. This innovative approach enables CTUs to handle block sizes of up to 64×64, surpassing the 4×4 to 16×16 block sizes of macroblocks.
As a result, H.265 achieves superior compression efficiency by efficiently processing larger blocks of information. The utilization of CTUs in H.265 empowers it to compress data more effectively, leading to enhanced video quality and reduced bandwidth requirements.
3. Bandwidth Optimization
With the exponential growth of streaming services, bandwidth optimization has become crucial for both content providers and viewers. The H.265 codec addresses this challenge by offering better bandwidth utilization.
By reducing the file size without compromising video quality, H.265 allows for the transmission of high-quality video content at lower bitrates. It ensures even over 50% less bandwidth consumption. This optimization reduces network congestion, minimizes buffering issues, and provides a smoother streaming experience.
It is particularly beneficial for streaming platforms catering to mobile users or regions with limited internet connectivity.
4. Device Compatibility
Another significant advantage of the H.265 codec is its broad device compatibility. Many modern devices, including smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, and streaming media players, support hardware acceleration for H.265 decoding.
This compatibility ensures seamless playback of H.265-encoded content without the need for additional software installations or device upgrades. As a result, content providers can reach a wide range of viewers across various devices, offering a consistent and high-quality streaming experience.
5. Future-Proofing and Industry Adoption
The H.265 codec is recognized as a significant advancement in video compression technology, and its adoption continues to grow rapidly across the industry. With its superior compression efficiency and support for higher resolutions, H.265 provides future-proofing capabilities.
Content providers can leverage H.265 to meet the evolving demands of higher quality video formats and resolutions, ensuring compatibility with future devices and platforms. The widespread adoption of H.265 as a standard codec by industry leaders and organizations further solidifies its position as a preferred choice for efficient video compression.
H.264 Vs H.265 Codec: A Comparative Overview
Now, in this comparative overview, we will delve into the differences between H.264 and H.265 codec.
1. Compression Efficiency
One of the primary factors to consider when evaluating video codecs is their compression efficiency. H.264, also known as Advanced Video Coding (AVC), has been widely used for quite some time and has proven to be highly efficient in compressing video content.
However, H.265, also referred to as High-Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), was introduced as an upgrade to H.264 with the promise of even greater compression efficiency.
2. Enhanced Compression Techniques
H.265 introduced several advanced compression techniques compared to H.264. These techniques include improved motion compensation, enhanced prediction algorithms, and more efficient coding structures.
While H.265 does offer superior compression techniques, the question arises whether the benefits outweigh the potential downsides.
3. Bandwidth and Storage Requirements
One significant advantage of H.264 is its ability to deliver high-quality video content while consuming lower bandwidth and requiring less storage space. This makes it an ideal choice for streaming platforms, especially in regions with limited internet infrastructure.
H.264 strikes a balance between quality and bandwidth/storage requirements, making it a more practical option for various applications.
4. Hardware and Device Compatibility
H.264 has been widely adopted across different devices and platforms, including smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, and gaming consoles. It has become the de facto standard for video compression due to its widespread support and compatibility.
On the other hand, H.265, being a relatively newer codec, faces limitations in terms of hardware support and device compatibility. This factor plays a crucial role in the codec’s adoption rate and makes H.264 the more favorable option for broader accessibility.
5. Power Consumption
H.264 has been optimized for power efficiency, making it suitable for battery-powered devices such as mobile phones and portable media players. With the increasing demand for video content consumption on mobile devices, power consumption is a significant concern.
H.264’s ability to deliver high-quality video while consuming less power gives it an edge over H.265 in terms of practicality and usability.
6. Industry Standard and Legacy Support
Given its widespread adoption and industry-standard status, H.264 has an extensive library of legacy content and hardware infrastructure built around it. This means that transitioning to H.265 would require significant investments in hardware upgrades and content re-encoding.
The cost and effort involved in this transition make H.264 the more viable and cost-effective choice for many businesses and content creators.
Suitability: HEVC vs. H.264, VP9, and AV1
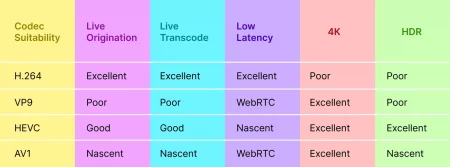
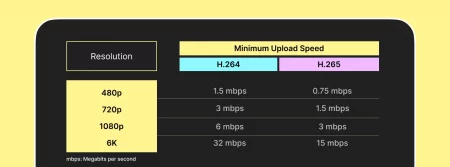
Minimum Upload Speed of H.264 Vs H.265
H.265 Codec in Streaming: Key Considerations
1. Adaptive Bitrate Streaming (ABR)
Adaptive Bitrate Streaming (ABR) is a key technique used in streaming to optimize the viewing experience based on the viewer’s available bandwidth. The H.265 codec integrates seamlessly with ABR technologies, allowing streaming platforms to dynamically adjust the bitrate and resolution of the video stream in real-time.
This ensures that viewers with varying network conditions can enjoy uninterrupted streaming without experiencing buffering or quality degradation. The combination of H.265’s compression efficiency and ABR provides a robust solution for delivering high-quality video content to a diverse range of viewers.
2. Encoding and Decoding Complexity
When considering the adoption of the H.265 codec, it is important to assess the encoding and decoding complexity associated with this technology. Compared to its predecessor H.264, H.265 encoding requires more computational power and time due to its advanced compression techniques.
Content providers and streaming platforms should ensure that their encoding and transcoding infrastructure can handle the increased complexity of H.265 encoding. Similarly, client devices should have sufficient processing capabilities to decode H.265-encoded content. By considering the encoding and decoding complexity, streaming platforms can ensure a seamless workflow and optimal performance when using the H.265 codec.
3. Content Delivery Network (CDN) Support
Streaming platforms often rely on Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) to efficiently distribute their content to viewers around the globe. When utilizing the H.265 codec, it is important to ensure that the CDN in use supports the delivery of H.265-encoded content.
This includes both the storage and delivery aspects of the CDN infrastructure. By selecting a CDN that is compatible with H.265, streaming platforms can effectively distribute their high-quality video content to viewers worldwide, ensuring a smooth and reliable streaming experience.
4. Transcoding and Multi-Format Support
In a diverse streaming ecosystem, it is common for content providers to offer their content in multiple formats to cater to different devices and platforms. When using the H.265 codec, it is essential to consider the transcoding requirements and multi-format support.
Content providers need to ensure that their transcoding infrastructure supports the conversion of H.265-encoded content to other popular codecs, such as H.264, to maintain compatibility with devices that do not support H.265.
This ensures that their content reaches a broader audience and can be accessed on various devices without compromising quality.
The Bottom Line
The adoption of the H.265 codec in streaming offers numerous advantages and considerations for content providers and streaming platforms. The H.265 codec’s superior compression efficiency allows for optimized bandwidth usage, reduced buffering, and smoother playback, even in low-bandwidth scenarios.
The integration of the H.265 codec with Adaptive Bitrate Streaming (ABR) enables dynamic adjustment of the video stream based on the viewer’s available bandwidth, ensuring uninterrupted streaming and optimal viewing experiences while H.264 codec offers even better compatibility.
And Muvi One, a top-notch OTT platform provider supports H.264 codec resulting in competitive streaming solutions for your end-users.
Yet to try it out?
Take a 14-day free trial today (no credit card needed).

FAQs
- What is the H.265 Codec, and how does it differ from other codecs?
The H.265 Codec, also known as High-Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), is a video compression standard that improves upon previous codecs like H.264. It uses advanced compression techniques to achieve higher compression efficiency and better video quality.
- What are the benefits of using the H.265 Codec for video compression?
The benefits of using the H.265 Codec for video compression include improved compression efficiency, which reduces bandwidth and storage requirements. It enables higher-quality video streaming, especially at lower bit rates, and supports high-resolution content, making it ideal for delivering immersive viewing experiences.
- Which devices and platforms support H.265 playback?
H.265 playback is supported by a wide range of devices and platforms. This includes modern smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, streaming devices, and popular video players. However, it’s important to note that the availability of H.265 support may vary depending on the specific device and its hardware capabilities.
- Is H.265 codec compatible with older devices and codecs?
While H.265 is compatible with many newer devices and codecs, it may not be universally compatible with older devices and codecs that lack the necessary hardware support. Older devices and software may require updates or additional software/plugins to decode and play H.265-encoded content.
- How does H.265 codec affect video quality and file sizes?
The H.265 codec offers improved video quality compared to previous codecs like H.264, especially at lower bit rates. It achieves this by utilizing more advanced compression techniques and efficient encoding algorithms. Additionally, it can reduce file sizes without significant loss of quality, making it suitable for streaming and storage purposes.

















Add your comment