Payment gateways are the unsung heroes of the streaming industry, seamlessly processing the financial transactions that grant viewers access to a world of digital content. Yet, within this dynamic sector, payment gateways have adapted and diversified to meet the unique needs of streaming services.
In this blog, we will break down the various types of payment gateways, shed light on their unique features, and help you make informed decisions that align with your business goals.
What is a Payment Gateway and Why is it needed for businesses?

A payment gateway is a technology that facilitates online and point-of-sale (POS) transactions by securely authorizing and processing payment transactions between a customer and a merchant. It plays a crucial role in the e-commerce ecosystem and is essential for businesses, especially those operating in the digital realm.
Streaming businesses often rely on subscription models, pay-per-view, or advertising revenue to generate income. Payment gateways facilitate the collection of payments from users for these services. They enable businesses to charge customers for access to premium content or services, helping to generate revenue.
Payment gateways make it easy for users to pay for streaming services. They offer various payment options, such as credit cards, debit cards, digital wallets, and more. This convenience can improve the user experience and encourage more people to subscribe to or purchase content from the streaming platform.
Payment gateways are responsible for handling sensitive financial information. They use encryption and security protocols to protect user data during transactions, reducing the risk of data breaches and fraud. This security is crucial for both the business and its customers.
Payment gateways often have built-in fraud detection and prevention mechanisms. They can flag or block suspicious transactions, reducing the risk of chargebacks and financial losses. Additionally, integrating Seon’s fraud detection software into your payment gateway can further enhance security measures, offering advanced tools to identify and mitigate fraudulent activities, thereby safeguarding against potential chargebacks and financial losses.
Types of Payment Gateways –
Payment gateways are essential components of e-commerce and online payment processing systems. They facilitate secure and efficient transactions between customers and businesses. There are various types of payment gateways, each with its own characteristics and use cases.
Let’s explore each type in detail:
Hosted Payment Gateways:
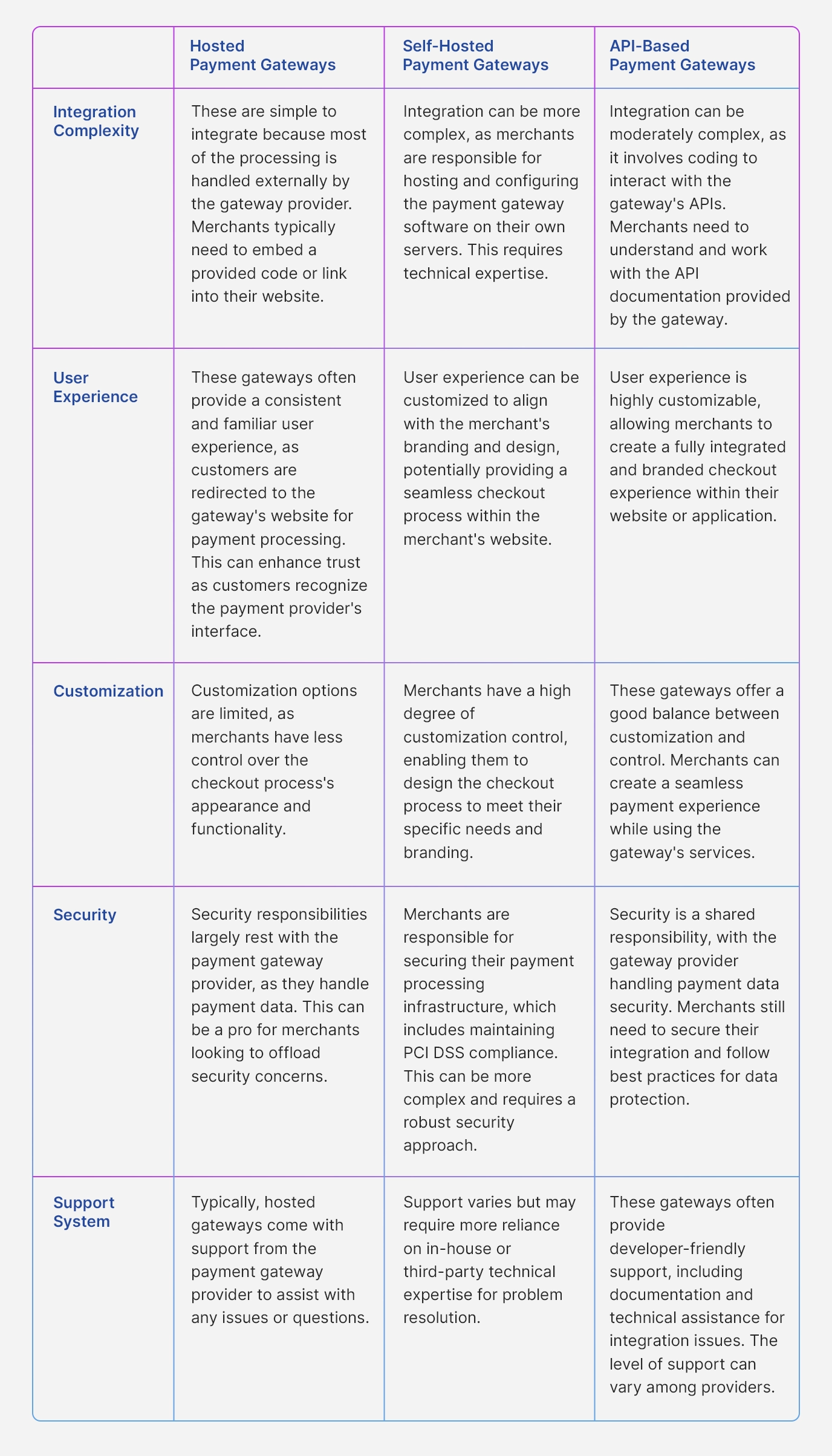
Hosted payment gateways are third-party services that handle the entire payment process on behalf of the merchant. When a customer makes a purchase, they are redirected to the payment gateway’s website to complete the transaction.
Pros:
- Simplicity: Easy to set up and use as most of the processing is done externally.
- Security: Payment data is handled by the gateway provider, reducing the merchant’s security responsibilities.
Cons:
- Limited customization: Merchants have less control over the checkout experience.
- Transaction fees: Payment gateway providers often charge transaction fees.
Examples: PayPal Standard, Stripe Checkout, and Square.
Self-Hosted Payment Gateways:
Self-hosted payment gateways are solutions that merchants install and host on their own servers. They have more control over the payment process and can customize it to align with their brand and website design.
Pros:
- Customization: Merchants can tailor the checkout process to their specific needs.
- Lower transaction costs: Reduced or no transaction fees compared to hosted gateways.
Cons:
- Technical expertise required: Merchants need to manage and secure their payment processing infrastructure.
- Compliance: Maintaining Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) compliance can be a complex task.
Examples: WooCommerce with various payment plugins, including the WooCommerce wallet plugin, and Magento with custom payment integrations.
API-Based Payment Gateways:
API-based payment gateways offer a balance between hosted and self-hosted gateways. They provide a set of APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) that allow merchants to integrate payment processing into their websites or applications while maintaining control over the checkout experience.
Pros:
- Customization and control: Merchants can create a seamless payment experience while using the gateway’s services.
- Security: API gateways typically handle security and compliance concerns.
Cons:
- Development effort: Integration may require coding and technical skills.
- Costs: Transaction fees and sometimes setup fees may apply.
Examples: Braintree, Authorize.Net, and Adyen.
Local Bank Integration:
This type of payment gateway integrates with local banking systems, allowing merchants to process payments directly from customers’ bank accounts. It is common in regions where traditional banking methods are prevalent.
Pros:
- Local payment support: Suited for regions where customers prefer bank transfers over credit cards.
- Potentially lower fees: Local bank payment gateways may have lower transaction fees.
Cons:
- Limited international support: May not be ideal for businesses targeting global customers.
- Integration challenges: Working with multiple local banks can be complex.
Examples: iDEAL (Netherlands), GiroPay (Germany), and Boleto Bancário (Brazil).
What are the Differences Between Hosted, Self-hosted and API-Based Payment Gateways?
Importance of Payment Gateway in e-commerce and Online Transactions

Payment gateways play a crucial role in the success of e-commerce and online transactions. They provide a secure and efficient way to handle payments, ensuring that customers can make purchases with confidence while offering several advantages, such as:
Security:
Payment gateways are designed to protect sensitive financial information. They use encryption and other security measures to ensure that payment data remains confidential during transmission. This is vital for safeguarding both the customer’s personal information and the merchant’s sensitive data.
Fraud Prevention:
Payment gateways often incorporate financial fraud detection tools and algorithms to identify and prevent fraudulent transactions. They can detect unusual patterns and flag potentially suspicious activity, which helps protect both the customer and the merchant.
Global Reach:
Payment gateways enable businesses to accept payments from customers around the world. They support various payment methods and currencies, making it easier for businesses to expand internationally and reach a broader customer base.
Convenience:
Payment gateways make the purchasing process more convenient for customers. They allow for various payment methods, such as credit cards, debit cards, digital wallets, and even bank transfers, giving customers flexibility in how they want to pay for their purchases.
Payment Processing:
Payment gateways facilitate the flow of funds from the customer to the merchant. They handle the authorization, capture, and settlement of transactions, streamlining the payment process and ensuring that merchants receive their funds promptly. Businesses that need a more integrated approach can try PayFac as a service to not only process transactions but also onboard sub-merchants under a single master account, reducing compliance burdens and accelerating payment acceptance
Multiple Currencies:
E-commerce businesses with a global customer base benefit from payment gateways that support multiple currencies. These gateways automatically convert the transaction amount into the customer’s preferred currency, making it easier for customers to understand the cost of their purchases.
Real-Time Transactions:
Payment gateways process transactions in real-time, which means customers receive immediate confirmation of their purchases. This quick feedback helps build trust and allows businesses to manage their inventory and order fulfillment more efficiently.
Integration of a New Payment Gateway in Muvi – Factors to take into Consideration
Integrating a new payment gateway into Muvi, a platform for OTT and video streaming services, involves various factors to ensure a smooth and effective payment processing system. Here’s an explanation of each of the key considerations:
Settlement/Processing Country/Currency:
- Country: Ensure that the payment gateway supports transactions in the countries where your audience is located.
- Currency: The payment gateway should support the currency in which you offer your content, as well as the currency your customers prefer. Multi-currency support may be necessary.
Payment Methods:
Credit Card/Debit Card/UPI: Consider the most popular payment methods in your target regions. The payment gateway should support these methods to cater to a wide range of customers.
Monetization Model:
- Subscription: If you offer subscription-based content, the payment gateway should handle recurring payments, automated renewals, and the ability to upgrade or downgrade plans.
- Pay-Per-View (PPV): For PPV content, ensure the gateway supports one-time payments for individual pieces of content.
Monetization Generic UX:
- Plan Update/Disable: Users should be able to upgrade or downgrade their subscription plans or disable their subscriptions easily.
- Success/Fail Scenarios: Implement a user-friendly experience for successful payments and clear error messaging for failed transactions to reduce user frustration.
Integration:
Webhook/API: Decide on the integration method. APIs offer more control and customization, allowing seamless integration with Muvi’s backend. Webhooks are useful for real-time updates, like confirming payments.
Promotional Features like Coupons:
Coupon Codes: The payment gateway should support the application of coupon codes for discounts and promotions, helping to attract and retain customers.
When integrating a payment gateway into Muvi, it’s essential to consider not only the technical aspects but also the user experience. Ensure that the payment process is seamless, secure, and user-friendly. Here are some additional factors to consider:
Security: The payment gateway must comply with security standards like PCI DSS to protect sensitive customer data.
Scalability: Ensure that the payment gateway can handle increased transaction volumes as your subscriber base grows.
Error Handling: Implement robust error handling to address issues like declined cards, expired cards, and other payment failures.
Testing: Thoroughly test the payment integration in a sandbox or staging environment to catch and fix any issues before going live.
Customer Support: Evaluate the quality of customer support provided by the payment gateway provider. Quick and efficient support is crucial when dealing with payment-related issues.
Legal and Compliance: Ensure that the payment gateway complies with all relevant laws and regulations in the countries you operate in.
Reporting and Analytics: Access to transaction data and analytics is essential for monitoring the performance of your payment processing system.
Ending Notes:
Muvi One is compatible with over 10 top-tier payment gateways worldwide, including FirstData, Stripe, Paypal Pro, Razorpay, Paypal Express, M-Pesa, Authorize.net, Stripe SCA, Giropay, Sofort, and more.
With Muvi One, you have the flexibility to configure multiple payment gateways, catering to diverse geographic audiences and offering various payment methods, all within a multi-currency framework. Our unwavering commitment to transaction and data security is evident through the implementation of a range of enterprise-grade security features, ensuring the utmost protection of data and privacy when handling payments on your platform. Start a free trial to explore the seamless integration process of multiple payment gateways on your Muvi-powered video streaming platform.


















Add your comment