Whether it’s catching up on the latest TV shows, attending a virtual event, or tuning in to a live sports game, the ability to stream multimedia content in real-time is critical. Real-Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP) is one of the many protocols that enable seamless multimedia streaming over the internet.
It provides the backbone for video conferencing, webinars, online gaming, and much more. However, with several streaming protocols available, understanding RTSP and its benefits can be overwhelming.
In this blog, we will take an in-depth look at Real-Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP), explore its uses and advantages, and provide practical insights on how to implement it in your live streaming workflows.
By the end of this blog, you will have a comprehensive understanding of what RTSP is, how it works, and why it’s critical for real-time multimedia streaming.

What Is a Protocol?
Protocols establish a set of guidelines that govern the transfer of data between different communicating systems. An example of this is the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), which defines the transmission of webpage data and hypertext links across the World Wide Web by regulating the communication between web servers and browsers.
Streaming protocols, on the other hand, are responsible for managing the distribution of live and on-demand streaming content. The streaming protocol suite includes RTSP, which serves as a fundamental technology for this purpose. RTSP’s primary role is to create and maintain sessions between the streaming server and the source.
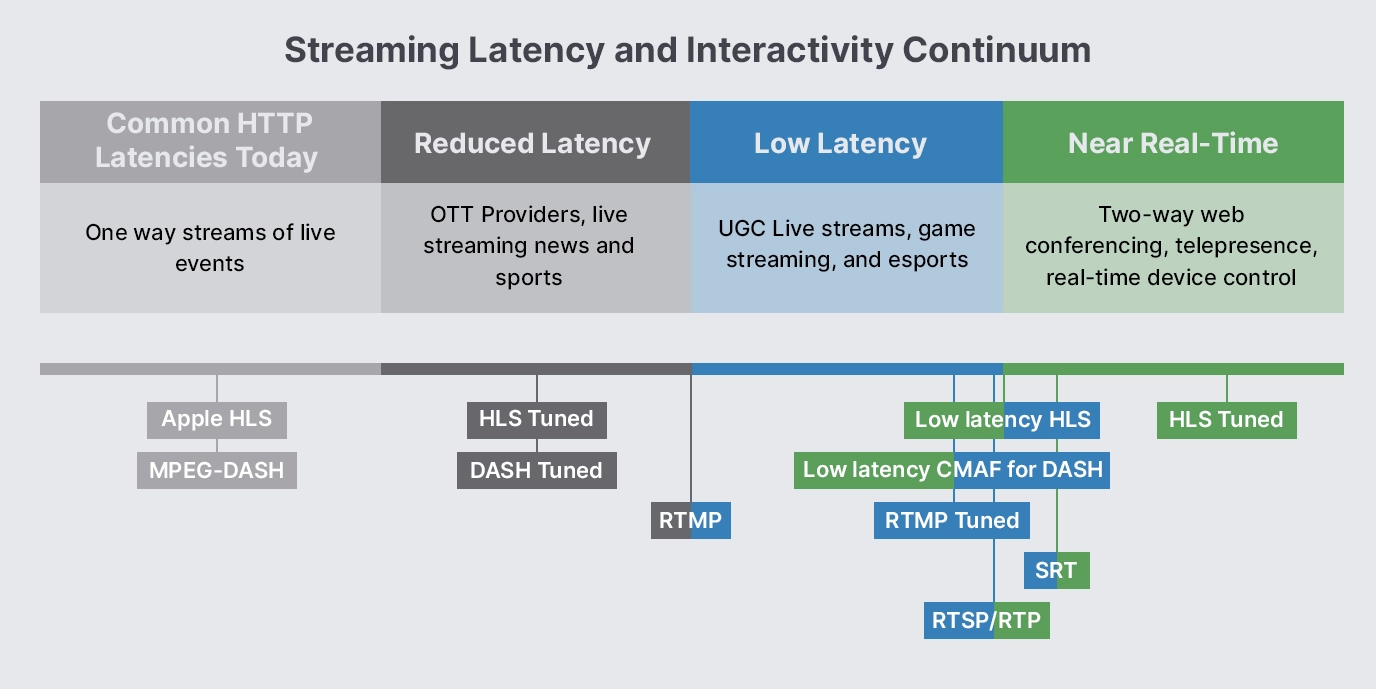
How does RTSP protocol work?
RTSP works on a client-server model, where the server streams the media content and the client sends commands to the server to control the flow of the content. The protocol operates over a reliable transport protocol such as TCP or a faster but less reliable transport protocol such as UDP.
Here is a basic overview of how RTSP works:
- The client establishes a connection to the server using the RTSP protocol.
- The client sends a request to the server to stream a particular media file or content.
- The server responds to the request, providing details such as the media type, encoding, and location.
- The client sends a PLAY command to the server to begin streaming the media content.
- The server begins streaming the media content to the client.
- The client can control the stream by sending commands to the server to pause, resume, or stop the stream.
- Once the client is done streaming the media content, it sends a TEARDOWN command to the server to end the session.
RTSP enables users to control the streaming of multimedia content through various commands such as play, pause, setup, etc. It also provides information about available options to the client through the “OPTIONS” command.
Users can watch, cue up, or shut down the stream based on the allowed parameters. RTSP maintains an end-to-end connection with TCP and achieves higher transmission speeds by keeping the data spigot open through this stable connection, eliminating the need for local downloading or caching.
Also Read : Streaming Protocols – Everything you need to know
RTSP in Brief
- Supported Audio Codecs: AAC, AAC-LC, HE-AAC+ v1 & v2, MP3, Speex, Opus, Vorbis
- Supported Video Codecs: H.265 (preview), H.264, VP9, VP8
- Playback Compatibility: Limited, with support from Quicktime Player, RTSP/RTP-compliant players, VLC media player, and 3Gpp-compatible mobile devices
- Benefits: Widespread adoption in IP cameras, with low latency
- Drawbacks: Not optimized for quality of experience or scalability
- Latency: 2 seconds
- Variant Formats: RTSP is an umbrella term encompassing the entire stack of RTP, RTCP (Real-Time Control Protocol), RTSPS (RTSP over SSL / Secure RTSP), and traditional RTSP
History of RTSP Streaming
Real-Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP) was first introduced in 1998 by RealNetworks as a means of streaming media over the internet. It was designed as an open standard for controlling streaming media servers and clients, allowing users to control the delivery of multimedia content over IP networks.
In the early days of RTSP, streaming media was still in its infancy, and the internet was not yet capable of reliably transmitting large amounts of data. As a result, early RTSP implementations were limited in scope and primarily used for delivering low-resolution video and audio.
Despite these limitations, RTSP quickly gained popularity due to its flexibility and ease of use. The protocol’s ability to handle both live and on-demand streaming made it a versatile tool for delivering multimedia content over the internet.
Over the years, RTSP continued to evolve and improve. The protocol was updated in 2002 with the release of RTSP 2.0, which added support for new media formats and improved support for streaming over unreliable networks.
Today, RTSP is widely used for streaming media over IP networks. It is commonly used in security cameras, live video streaming, and other applications that require low-latency, real-time media delivery.
However, RTSP has also faced challenges as new streaming technologies have emerged. Some of these technologies, such as HTTP-based streaming protocols, have been optimized for better quality of experience, scalability, and compatibility with existing web infrastructures.
Also read : Comparing Low Latency Streaming Protocols: SRT, WebRTC, LL-HLS, UDP, TCP, RTMP
RTSP vs. Other Streaming Formats
Which streaming format is currently being used more?
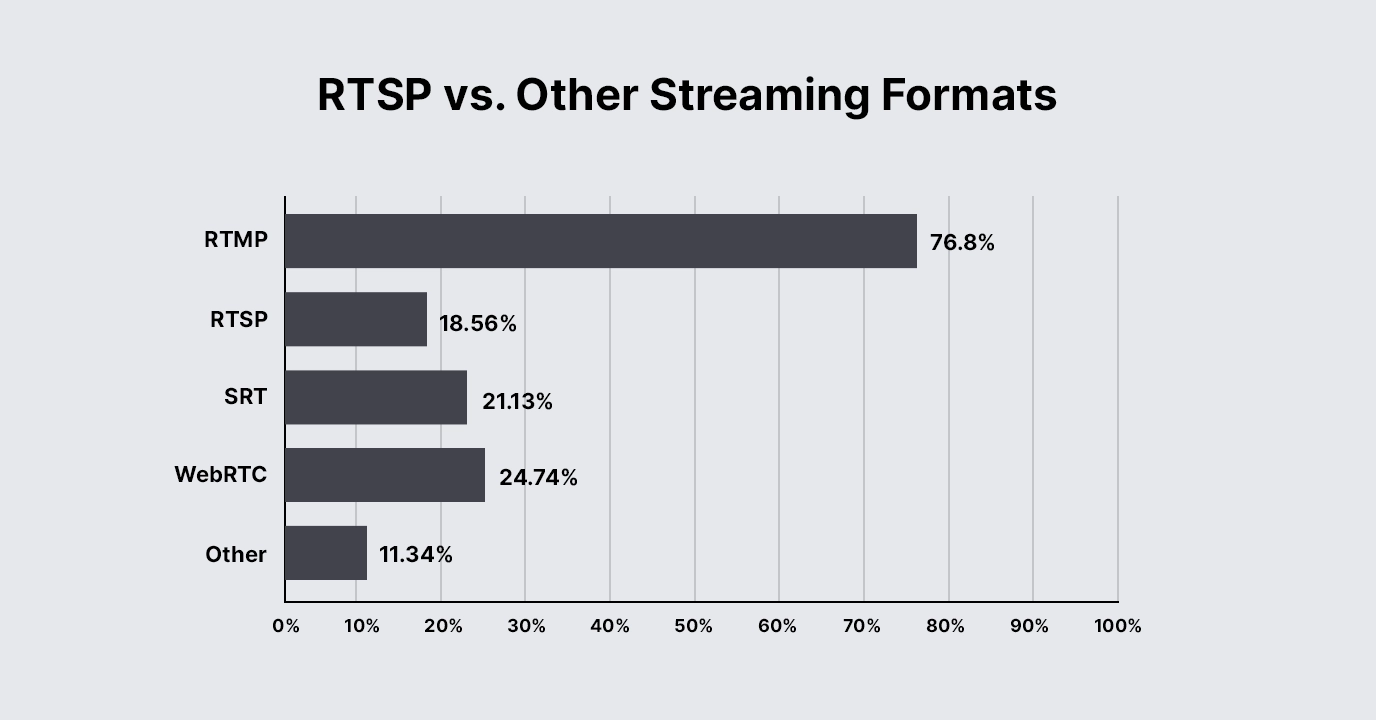
Comparison of RTSP vs. Other Streaming Formats
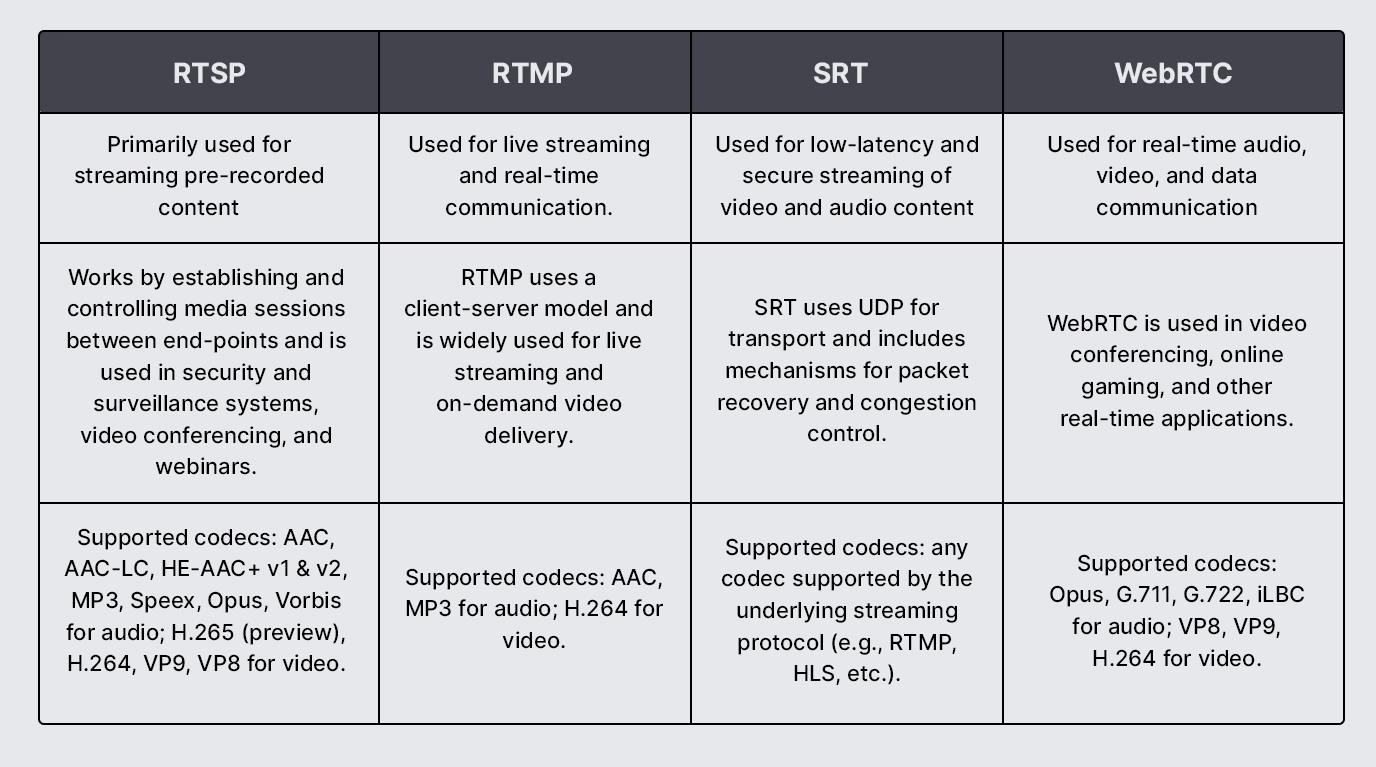
Applications of Real Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP)
Use in streaming multimedia content
- RTSP is used streaming multimedia content in real time, such as live events, sports, news, and entertainment
- RTSP enables users to receive and play live video and audio streams on their devices.
Applications in the security and surveillance industry
- RTSP is used for applications in the security and surveillance industry, such as live video feeds from security cameras, video recording and playback, and remote access to cameras.
- It allows for real-time video streaming and recording, enabling users to monitor and manage security cameras in real time.
Use in video conferencing and webinars
- Use in video conferencing and webinars, allowing for real-time video and audio communication and collaboration
- RTSP enables users to participate in online meetings, video conferences, and webinars in real time, without any delays or interruptions.
Using Muvi One as Your RTSP Server
Although RTSP is an older protocol, it remains a popular ingest format. However, to ensure successful delivery of the stream to end-user devices, a video repackaging solution is necessary.
To achieve this, RTSP servers can be used to convert live RTSP streams into other formats for playback. One option is to use media server software or services, which can offer more than just repackaging. For example:
- Repackaging an RTSP stream into HLS for large-scale delivery
- Utilizing WebRTC to maintain sub-second delivery
- Implementing adaptive bitrate streaming to optimize video quality for varying network conditions
- Adding security features like encryption and access control to protect content
- Integrating with content delivery networks (CDNs) to improve scalability and reliability
By using a media server with RTSP, you can enhance the functionality and delivery capabilities of your video content.
Muvi One is a versatile platform that can accommodate any type of streaming architecture you want to create. Our comprehensive service offers end-to-end support, ensuring reliable performance throughout your workflow. To experience the power of Muvi One for yourself, sign up for a free trial today.
Also read : RTMP vs. RTSP: How to Choose Your Streaming Protocol

FAQs
What is Real-Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP)?
Real-Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP) is a network protocol used for controlling the delivery of real-time multimedia data, such as audio and video, over IP networks. It enables the establishment and control of media sessions between a server (streaming media source) and a client (streaming media player). RTSP operates in a client-server architecture, where the client sends requests to the server to initiate, pause, resume, or terminate a streaming session.
How does RTSP protocol work?
RTSP works on a client-server model, where the server streams the media content and the client sends commands to the server to control the flow of the content. The protocol operates over a reliable transport protocol such as TCP or a faster but less reliable transport protocol such as UDP.
What are the benefits of using RTSP for streaming?
Using Real-Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP) for streaming offers several benefits:
- Efficient Control
- Flexibility
- Interoperability
- Real-Time or Near-Real-Time Delivery
- Scalability
- Stream Control and Synchronization
How is RTSP different from other streaming formats?
RTSP primarily focuses on the control aspect of streaming, providing a standardized protocol for initiating, pausing, resuming, and terminating streaming sessions. It is responsible for session setup and management. On the other hand, other streaming formats like RTP (Real-Time Transport Protocol) and HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) handle the actual transport of media data.
What are the common applications of RTSP?
The three most common applications of RTSP are:
- Used in streaming multimedia content
- Used in the security and surveillance industry
- Used in video conferencing and webinars
















Add your comment