Digital Rights Management (DRM) is a method of securing digital video content to prevent piracy and unauthorized usage of the videos and other content types. DRM ensures that video is stored and transmitted in an encrypted form to deliver it for the authorized users and their devices. A DRM system allows a lot more sophisticated functionality in which your content is protected in all possible aspects. As DRM is a bit complex concept to understand, we like to demystify the DRM with a series of blogs. Here is our first one to dig in a bit deeper beyond the basics.
Choosing a content protection system
The creation and production of video content requires a lot of time, effort, and investment. And without proper security measures, it may lead to piracy and unauthorized usage, affecting overall revenue and efforts. So, choosing a content protection system is the key to monetize and secure your content successfully.
There should be a balance between the strength of protection and barriers to reach viewers when considering content protection. Besides other options like Tokenization, encrypted streaming, and the illicit distribution of digital video content, DRM stood at the top of the list, ensuring better content security, especially for the Digital streaming platforms.
What does DRM mean in the video playback context – Standard encryption Vs. DRM encryption?
DRM is commonly mistaken for being equal to encryption; the encryption part actually carries in the packager, which is a common part of the encoder, standalone, and a part of the Content Delivery Network.
When you look at DRM in a video playback context, it means many things; it’s all about the encryption and device protocols maintained by video platforms to protect or secure their video content from being pirated or misused.
To understand the video DRM in a better way, you should understand video encryption and how it relates to the DRM. Video encryption is a process of conversion of video into a non-video secure format. So, viewers cannot directly access the raw file. A standard video encryption technology, like HLS E, RTMP E, and AES 128, has critical exchange mechanisms that are very prone to hacking and downloading, averting the purpose of encryption.
DRM protects the encryption key by preventing easy access to a hacking software. It plays a dual role in encrypting the video and protecting the video encryption key. There are many commercial DRM systems available in the market, and at least the professional DRM works with AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) as the encryption technique.
AES – Advanced Encryption Standard
AES is a standard encryption of digital video content and other content types which utilizes symmetric encryption technique, i.e.creates duplicate keys used for encryption and decryption of the content.
AES is widely used in commercial data packagers and DRMs today and is available in different types for video content encryption. CTR and CBC are the primary modes of AES. Both are different in the encryption process and how they are being used.
The critical aspect you need to consider while encrypting the video is to get the best ratio between encryption time, effort, and security. Encrypting the videos is a bit resource-demanding and consumes time, making it hard to do in remote edge servers.
How does DRM work?
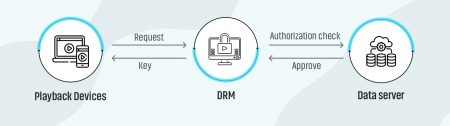
The DRM workflow is initiated with the content being encrypted and packaged for delivery. When a customer clicks on the video play button to play, the player requests the key to access the content from the license server. The server determines whether the video players and devices are authorized or not before responding with a decryption key. When the authentication process gets complete, the player can decrypt the video and start playback for the customers. It happens almost instantly.
A Detailed Workflow of DRM:
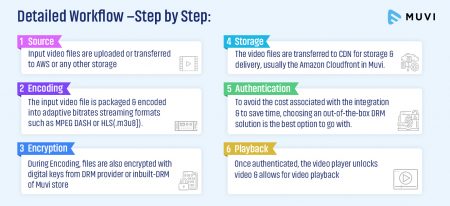
DRM in Muvi
At Muvi, we use a Studio Approved DRM solution. The license key and the content key is unique for each DRM account and content, respectively. Once Encoding is done, we upload the video to the S3 bucket. MPD format. End-user browses and plays content with Muvi’s proprietary HTML5 player with Amazon Cloud front CDN URL for the content. It points towards MPEG-DASH video stored in a respective S3 bucket. When the end-user browses for the content, we select the DRM license to depend on the browser. If DRM processes the license key and is authenticated successfully, then the content plays to the end-user.
If you are planning to create your own over-the-top platform with high-security DRM, Muvi is the best choice to ensure the security of your video content. Try a 14-day free trial today













Add your comment