In this era of piracy, protecting your video content is the key. And Digital Rights Management or Video DRM plays a key role in content protection. Though it is slightly complicated technically, you must have a thorough understanding of it as video streaming entrepreneurs.
In this blog, we will cover everything you need to know about DRM so that it becomes easier for you to implement and work with video DRM as a streaming entrepreneur. So, let’s begin by defining what DRM is and what it technically means.
What Does DRM Mean?
Going by the literal meaning, DRM stands for “Digital Rights Management”. It helps you protect any form of digital content from any form of misuse. In simpler words, it helps you protect the intellectual property rights of the digital content created and published by you so that no one can steal or reuse your content in any manner possible.
So, why is it important?
If you want to generate revenues from your videos, it is important that they reach the viewers who are willing to pay you the price needed for it. But in this era of piracy, the pirates often try to steal your content and then release it online from their end, so that they can earn from them. As a result, you often lose out on potential viewers, who get access to the content released by the pirates. Hence, it decreases your revenue considerably.
To avoid such unwanted losses, it is important to ensure that your content is safe from piracy. And video DRM, User Authentication, Geo-Blocking, and Forensic Watermarking help ensure the same.
What is the Role of DRM in Video Playback?
DRM technology plays a huge role in protecting your online video content. It does not allow unauthorized devices and unauthorized users to access the content, as the DRM Key (which we will explain in our next few sections) is delivered to the authorized devices and user accounts only.
Also, most of the video DRM technologies implement screen recording protection, which makes content stealing difficult for the pirates. Hence, DRM itself offers two-way protection, by restricting the content access and encrypting it, along with preventing any form of content recording and reuse.
Fundamentally, DRM plays the following four major roles in video playback:
- Encryption: DRM encrypts the video content using a special set of DRM keys, and then transfers the encrypted data over the internet. Hence, the pirates fail to steal the content when it is en route from the server to the end-user’s device.
- Watermarking: Unlike visible watermarking which can be easily removed through video editing, forensic watermarking is embedded into the metadata of the video and hence it cannot be altered easily.
- User Licensing: DRM often handles the distribution of video content by issuing a license to the eligible content viewers who can access the content. It helps in keeping the unwanted users away from your content.
- User Authentication: DRM gives access to your content to authenticated users only.
What is DRM Encryption?
We usually “Encrypt” any digital content to keep it safe from unwanted access. Actually, it can be considered as a form of digital lock. During Encryption, the original content is encoded (read converted) into an alternative form of data. And that alternative data is transferred from the server to the user’s devices via the internet or any other form of network. This end-user device knows how to “Decrypt” this content.
Now in the case of DRM, this encryption is done using a special DRM key, which can be decrypted using the corresponding DRM decryption key only. This key is delivered to the authentic end-user’s device from a special DRM server just before the video playback. Hence, DRM Encryptions are always more stronger and difficult to decrypt without the right key on the right device.
How Does DRM Work?
Technically, in a DRM-enabled system, the content has to go through multiple servers and processes that ensure its safety. The technical workflow diagram of a DRM-enabled system is given below:
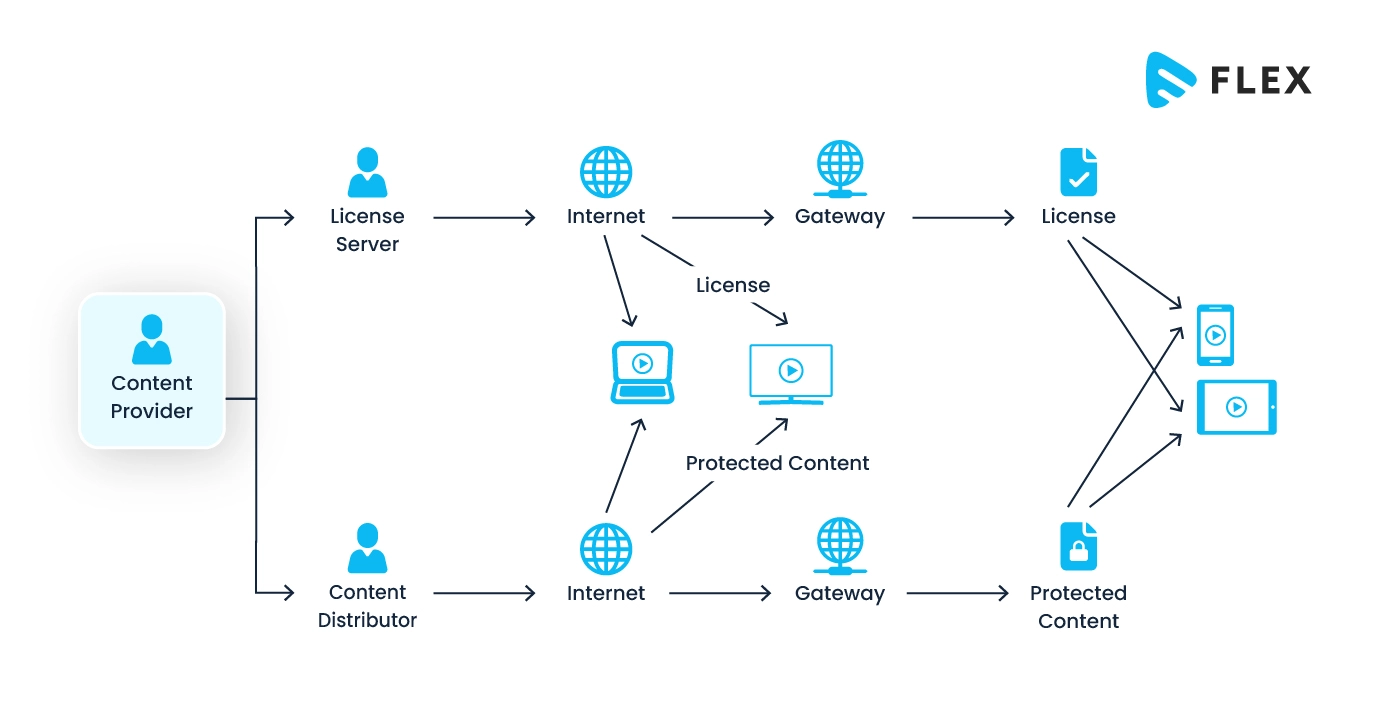
The step-by-step process is explained below:
- Content Creation and Uploading: The content curator and uploaders upload digital such as music, videos, or ebooks into the system.
- Encryption of Content: The uploaded content is then encrypted to make it unreadable while it is transferred online.
- Distribution of Content: This encrypted content is then distributed to various channels, such as online stores, streaming platforms, or download services, which act as an interface for the users.
- User Purchase/Access Request: When the users get to view the available content on the streaming platforms or other places where it was distributed, they either purchase or request access to the content.
- License Request: In this step, the user’s device or software sends a request for a license to the DRM license server. The device cannot play the content until and unless it receives that license.
- Authentication: On receiving the license request, the DRM server first authenticates the user and its device to verify the legitimacy of the request.
- License Generation and Delivery: If the request is found authentic, the license server generates a license that includes decryption keys and usage rights of the content. This license is then delivered securely to the user’s device.
- Decryption: The user’s device uses the decryption keys from the license to decrypt the content.
- Content Playback: The user’s device can now play the decrypted content.
Here, we need to note that the DRM system enforces certain “Usage Rights”, which are delivered to the end-user device along with the license. This ensures that the content is used in accordance with the terms defined in the license.
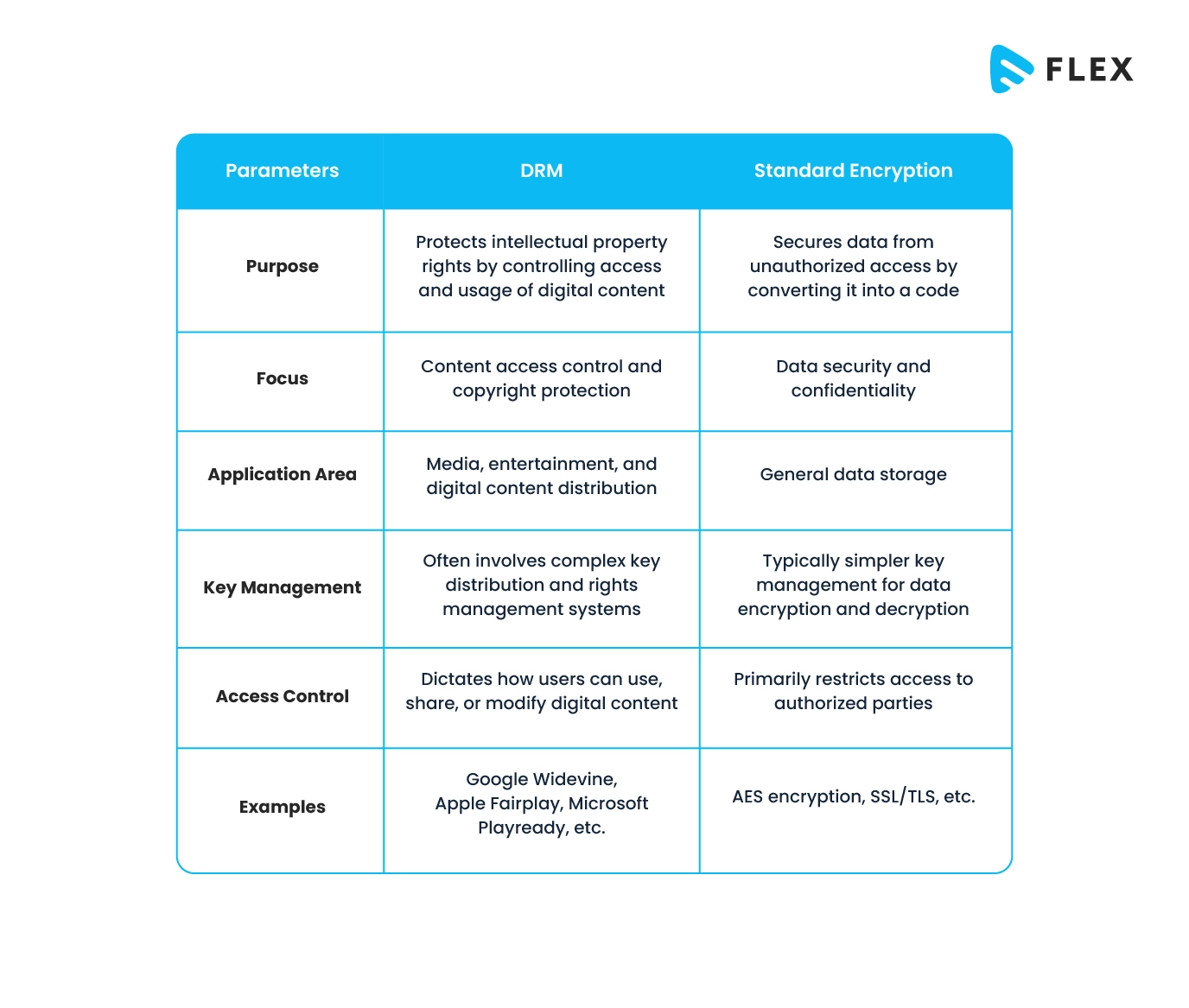
Why is DRM Better than Standard Encryption?
DRM and Standard Encryption are two completely different modes of encrypting digital content that serve different purposes.
DRM is specifically designed to protect the intellectual property rights of your digital content. It ensures that the content cannot be misused by those who do not hold the rights to do so. It primarily focuses on controlling access and usage of digital content.
On the other hand, Standard Encryption primarily focuses on securing data from unauthorized access. It is not a digital rights management tool, rather it is a data protection tool, often used to protect leakage of data.
The major differences between the two have been tabulated below:
Types of DRM Systems
There are multiple different types of DRM Systems, with their features and characteristics. Some of the most popular ones are discussed below.
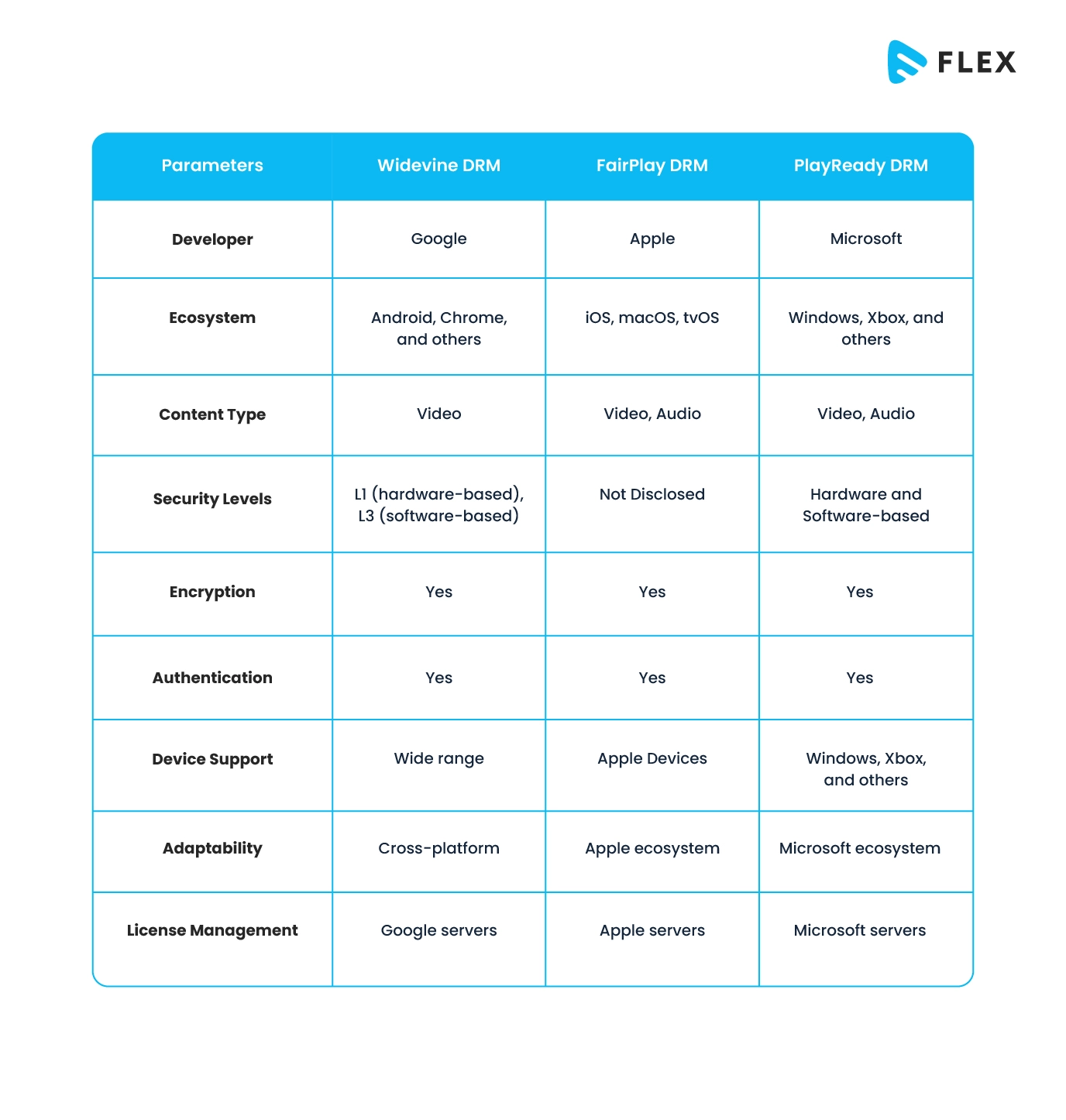
Google Widevine DRM
Google Widevine DRM is a digital rights management system developed by Google. Its main purpose is to protect digital content from unauthorized access and distribution. It is commonly used in streaming services to secure video content.
Widevine provides different security levels, including L1 (hardware-based) and L3 (software-based). However, please note that the application of these levels solely depends on the device’s capabilities. The different security levels help video streaming entrepreneurs deliver high-quality encrypted content, thereby protecting them from piracy.
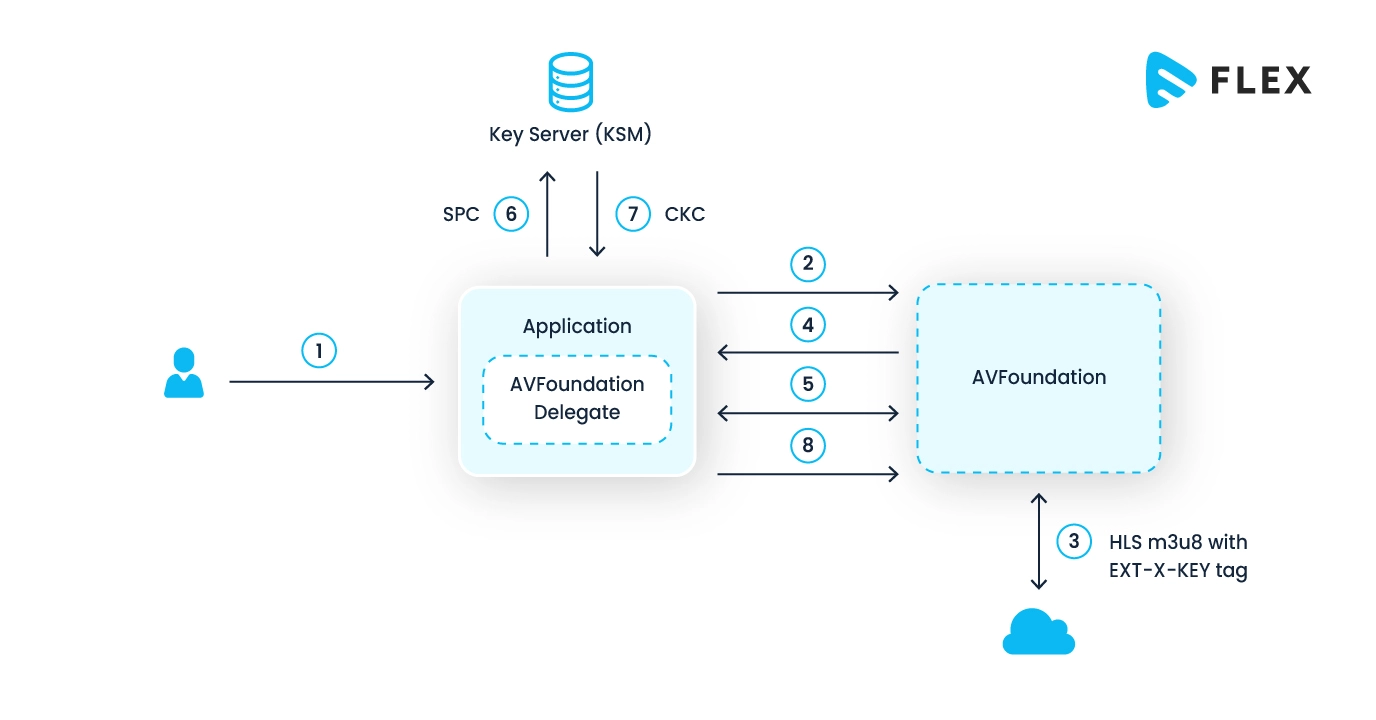
Apple Fairplay DRM
Apple FairPlay DRM is designed by Apple to protect digital content present within its ecosystem. It employs encryption to secure media files. It also ensures that only authorized devices can access and play the content.
The sole purpose of FairPlay is to prevent unauthorized copying and distribution of copyrighted material. Thus, it offers video streaming entrepreneurs a way to control access to their digital assets on Apple platforms. This is particularly very useful for video curators, as their videos remain safe from piracy.
The technical architecture of Apple Fairplay DRM is given below:
Microsoft PlayReady DRM
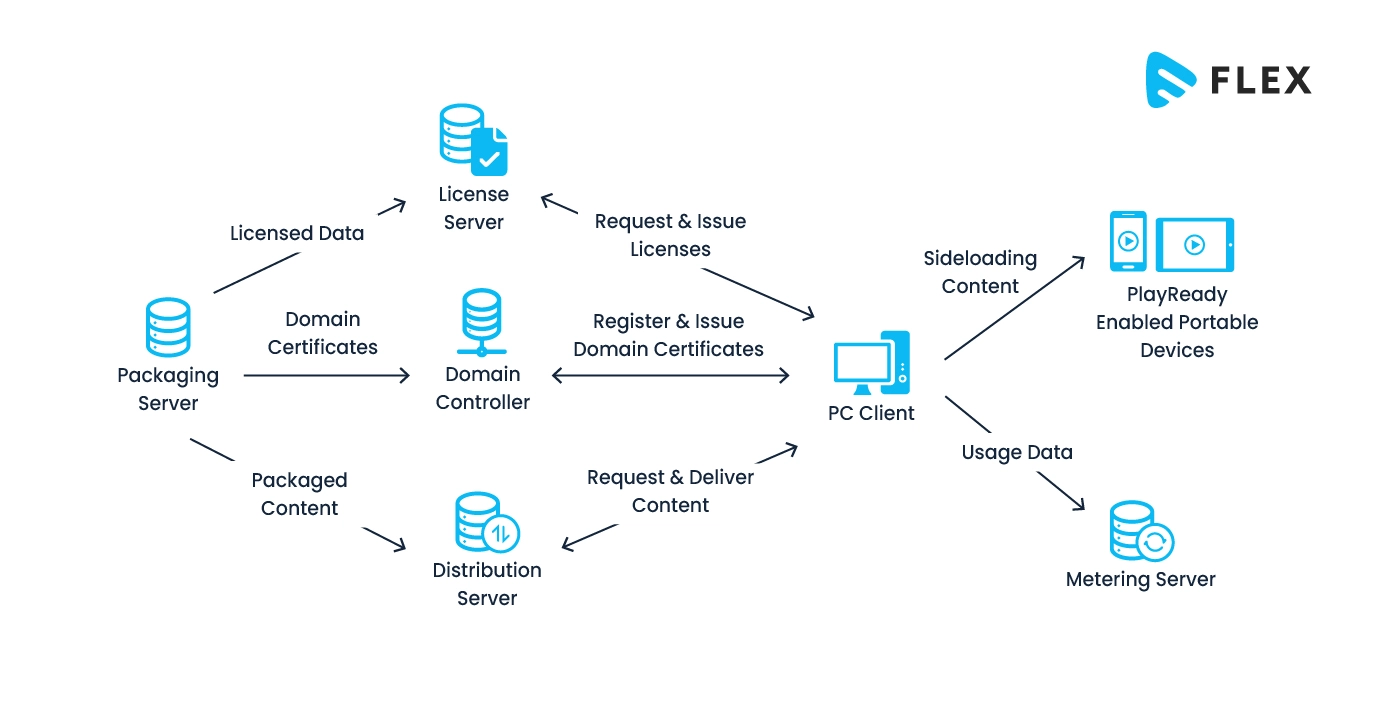
Microsoft PlayReady DRM was developed by Microsoft. Like other DRMs, it also aims to safeguard and control access to digital content. Its main purpose is to prevent unauthorized use, distribution, and copying of copyrighted material.
PlayReady is known to support a wide range of content types, including audio and video. That is why it is often used in streaming services, online video platforms, and other digital distribution channels.
Technically, PlayReady utilizes encryption, licensing, and secure playback mechanisms to protect content on various devices and platforms that support this DRM technology. Its technical workflow diagram is given below:
Widevine vs Fairplay vs Playready – What’s the Difference?
Here’s a simplified comparison of Google Widevine DRM, Apple FairPlay DRM, and Microsoft PlayReady DRM:
What is Multi-DRM Support?
Till now, we have been trying to understand the individual DRM systems. But do you know that we can use all the DRM systems together? Yes, such a system does exist and is referred to as a Multi-DRM Architecture.
Technically, multi-DRM refers to the use of multiple DRM technologies to protect digital content across various platforms and devices. In a multi-DRM architecture, content is encrypted using various DRM technologies, and licensing servers are set up to issue licenses compatible with each DRM system.
How Does Multi-DRM Work?
If you go through the technical workflow of Multi-DRM, you will notice that it involves several keys and licensing servers, that ensure the secure delivery and playback of digital content across various platforms and devices. The workflow has been depicted in the diagram given below:
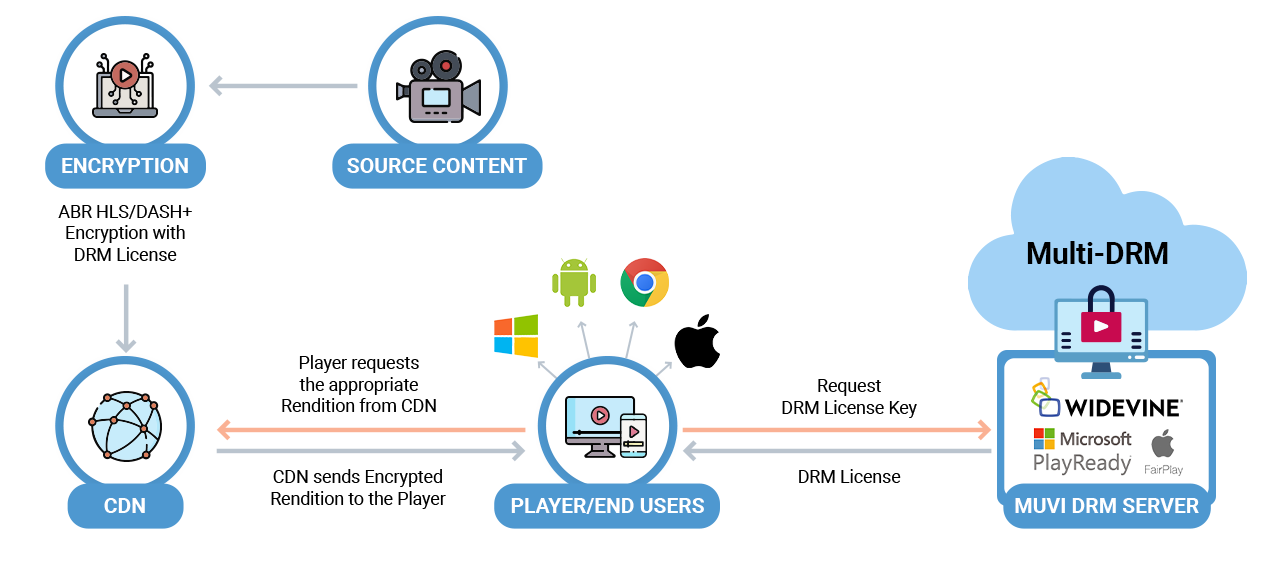
Here’s a basic overview of the Multi-DRM workflow:
- Content Encryption: The original digital content, such as video or audio files, is encrypted using multiple DRM systems. Each DRM system has its own encryption algorithm and keys.
- License Generation: For each DRM system used, a corresponding license is generated. These licenses contain encryption keys and usage policies specific to the DRM technology.
- License Delivery: The generated licenses are then delivered to the content delivery network (CDN) or streaming server. The CDN is responsible for distributing the encrypted content and associated licenses to end-users.
- User Authentication: When a user attempts to access the content, their device or application authenticates with the Multi-DRM service. This authentication ensures that the device is authorized to play the content.
- License Request: Upon successful authentication, the user’s device sends a license request to the Multi-DRM service. The request typically includes information about the device, the user, and the content being accessed.
- License Acquisition: The Multi-DRM service validates the request and issues the appropriate license for each DRM system used. These licenses contain the necessary decryption keys and usage rules.
- Decryption and Playback: The user’s device receives the licenses and uses them to decrypt the content. Once decrypted, the content can be played back on the device.
- Rights Management: The DRM systems enforce usage policies defined by video streaming entrepreneurs. These policies may include restrictions on the number of devices, concurrent streams, or expiration dates for the content.
Why is Multi-DRM Important?
Now comes the question, why would you use a multi-DRM system instead of a single DRM system? Well, Instead of relying on a single DRM solution, video entrepreneurs usually implement multiple DRM systems to ensure compatibility with a wide range of devices and ecosystems.
This approach allows them to reach a broader audience while addressing the diverse security requirements of different platforms. Multi-DRM enables the secure delivery of content to different devices and applications, regardless of the specific DRM technology supported by each platform. It’s a flexible solution that caters to the fragmented landscape of digital content consumption, accommodating the requirements of various devices and ecosystems in the market.
This is particularly important because you would usually want your video content to be played on different devices and ecosystems, but each of them supports different DRM technologies. Thus Mulit-DRM provides you the flexibility that is much-needed in today’s diverse digital landscape.
How DRM and Multi-DRM Secure Your Videos?
DRM and Multi-DRM solutions play a crucial role in securing video content by implementing various encryption and access control measures. Here’s how they contribute to the security of video content.
1. Encryption
- DRM: DRM systems encrypt video content using robust algorithms. This encryption makes it challenging for unauthorized users to access or distribute the content without the proper decryption keys.
- Multi-DRM: Employing multiple DRM technologies enhances security by diversifying encryption methods. Even if one DRM is compromised, the others provide an additional layer of protection.
2. Access Control
- DRM: DRM systems enforce access control policies. Users must authenticate and obtain a license to access the encrypted content, ensuring that only authorized users can decrypt and view it.
- Multi-DRM: With Multi-DRM, video streaming entrepreneurs can cater to the requirements of different devices and platforms, each with its own DRM support. This allows for a broader audience while maintaining access control measures.
3. License Management
- DRM: Licenses issued by DRM systems contain decryption keys and usage rules. These licenses are specific to the user, device, and content, providing a means to manage and enforce rights associated with the content.
- Multi-DRM: The generation and delivery of multiple licenses for different DRM systems allow video streaming entrepreneurs to address the diverse needs of their user base while maintaining control over content distribution.
4. Device Authentication
- DRM: DRM systems often require devices to authenticate themselves before obtaining a license. This ensures that only authorized devices can access the content.
- Multi-DRM: Supporting multiple DRM technologies enables video streaming entrepreneurs to accommodate a wide range of devices, each requiring its own authentication and authorization process.
5. Usage Policies
- DRM: Content providers can define usage policies within DRM systems, such as limiting the number of devices, and concurrent streams, or setting expiration dates for access to the content.
- Multi-DRM: By using multiple DRM solutions, video streaming entrepreneurs can implement diverse usage policies tailored to different platforms and devices, enhancing overall content security.
To Sum Up
DRM and Multi-DRM solutions work together to protect video content by employing encryption, access control, license management, device authentication, and customizable usage policies. This multi-layered video DRM approach helps deter piracy, and unauthorized distribution and ensures that content is securely delivered to legitimate users across various platforms.
At Muvi, video streaming entrepreneurs enjoy a built-in Multi-DRM infrastructure. We support Widevine, FairPlay, PlayReady, and more, so that your content remains 100% secured across all devices and ecosystems. So, if you are looking to create your video streaming platform, or searching for a reliable and secure video hosting platform, do not forget to try Muvi Ecosystem products.
Muvi One helps you create your own video streaming platform within minutes, without writing a single line of code! Packed with 100+ industry-leading features, our robust technical architecture helps you deliver buffer-free and highest-quality videos to your viewers across the globe.
Also, Muvi Flex – our exclusive video hosting solution helps you host, manage, and distribute videos securely across channels. We are one of the very few video hosting solutions that employ built-in Multi-DRM security. You can manage all your videos over a single CMS, and play them over your customized video players. Try it for yourself! Sign up to start your 14-day FREE trial.
DRM Glossary
- DRM License: A DRM license is a digital permission slip containing encryption keys and usage policies, granting authorized users the right to access and consume protected digital content.
- DRM License Server: A DRM license server is a centralized system that issues and manages digital licenses, controlling access to encrypted content by providing decryption keys and enforcing usage policies.
- DRM Encryption Key: A DRM encryption key is a cryptographic code used to secure and encode digital content.
- DRM Decryption Key: A DRM decryption key is a cryptographic key that allows authorized users, devices, or applications to decrypt and access protected digital content.
- Offline DRM: Offline DRM refers to a system that inserts DRM in offline content. It typically involves the issuance of licenses for content that is stored locally, enabling users to play the protected media offline for a specified period, after which reauthentication may be necessary.
- Chrome DRM: It employs Widevine DRM.
- Firefox DRM: Firefox primarily uses the Widevine Content Decryption Module for DRM support.
- Edge DRM: It employs PlayReady DRM.
- Safari DRM: It employs FairPlay DRM.
- Android DRM: It employs Widevine DRM.
- Windows DRM: It employs PlayReady DRM.
- iOS DRM: It employs FairPlay DRM.
- HLS DRM: HLS DRM refers to the integration of DRM technologies with the HLS streaming protocol. It involves encrypting and protecting video content delivered via HLS, ensuring secure and controlled access on compatible devices while preventing unauthorized distribution or consumption.
- Dash DRM: Dash DRM involves the combination of DRM technologies with the DASH streaming protocol. It focuses on securing and protecting video content delivered through DASH.
- HTML5 DRM: HTML5 DRM refers to the integration of DRM capabilities within the HTML5 standard for web content. This allows video streaming entrepreneurs to apply encryption and access controls directly to HTML5-based media elements (such as video and audio) to protect against unauthorized use and distribution.
- Content Decryption Module: A Content Decryption Module (CDM) is a component in a web browser that handles the decryption of encrypted media content protected by Digital Rights Management (DRM) systems. It is responsible for managing the decryption keys and enforcing access controls specified by the DRM, ensuring that only authorized users and devices can access and play the protected content. CDNs, such as Widevine for Chrome or PlayReady for Edge, are examples of CDMs used to enable secure playback of encrypted multimedia content in web browsers.






















Add your comment