Video content has become an integral part of our daily lives. From entertainment and education to marketing and communication, videos have the power to engage, inform, and inspire audiences worldwide. However, with the ever-increasing demand for high-quality video streaming across various devices and network conditions, delivering seamless and buffer-free experiences has become a significant challenge for content creators and distributors.
In this blog, we will know about Progressive Video Encoding, explore its principles, benefits, and practical applications. Whether you are a content creator, a developer, or simply curious about the future of video streaming, this blog is your gateway to understanding about Progressive Video Encoding.
The Need for Efficient Video Encoding Techniques
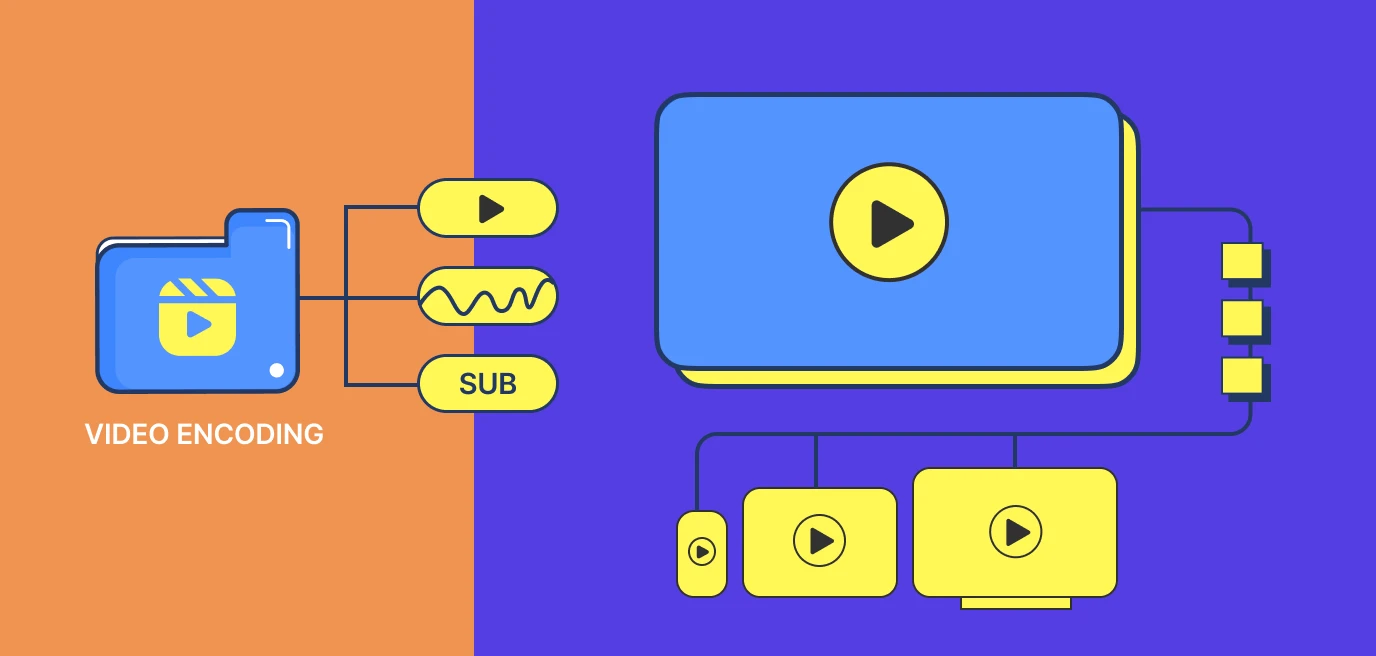
Video content is ubiquitous and demand for high-quality streaming experiences continues to soar, efficient video encoding techniques have become more critical than ever before. The sheer volume of video data being generated, transmitted, and consumed on various platforms presents a multitude of challenges that must be addressed to ensure optimal user experiences.
- Bandwidth and Network Constraints: With the rise of online video platforms, live streaming, and video-on-demand services, the need for efficient compression becomes apparent. High-resolution videos can be extremely data-intensive, leading to buffering issues and prolonged loading times, particularly in regions with limited internet connectivity. Efficient video encoding techniques are essential to reduce the data size without compromising on visual quality, making it easier to deliver videos across diverse network conditions.
- Multi-Device Compatibility: The proliferation of smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, and other connected devices necessitates adaptive video streaming. Content must be encoded in multiple resolutions and bitrates to accommodate various screen sizes and processing capabilities. By employing efficient encoding methods, content providers can ensure seamless playback across different devices while reducing storage and delivery costs.
- Storage and Cost Optimization: High-quality video files can be substantial in size, requiring significant storage space and increasing the expenses associated with hosting and distribution. Efficient video encoding enables content creators and distributors to maintain a balance between visual quality and file size, thereby optimizing storage and reducing operational costs.
- Enhanced User Experience: A smooth and buffer-free video streaming experience is crucial for engaging audiences. By employing advanced encoding techniques, content providers can minimize loading times and latency, leading to improved user satisfaction and retention rates.
- Eco-Friendly Practices: In an era where environmental consciousness is paramount, efficient video encoding can contribute to greener practices. By reducing data sizes and minimizing data transmission, less energy is consumed during video delivery, making it a more environmentally friendly choice.
- Real-Time Applications: Video content is not limited to entertainment; it has extensive applications in teleconferencing, remote learning, surveillance, and more. For real-time applications, where low latency is critical, efficient video encoding becomes indispensable.

The Role of Video Encoding in Video Streaming
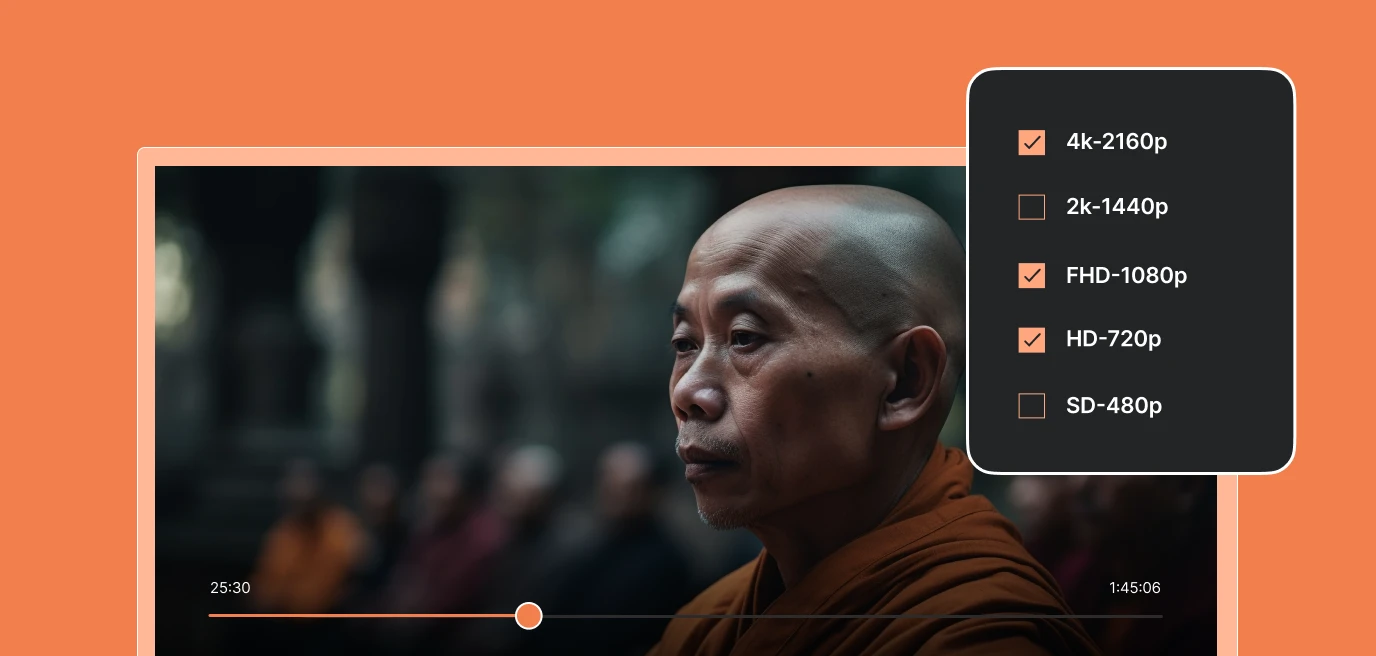
Video encoding plays a central role in video streaming, as it is the process of compressing video files into a digital format suitable for transmission over the internet. It is a vital step that ensures efficient data delivery and optimal playback quality for viewers. Let’s explore the key roles of video encoding in video streaming:
Compression:
Video files are often large and data-intensive, especially when they are recorded in high resolutions and frame rates. Video encoding uses compression algorithms to reduce the file size while preserving visual quality. By compressing the video, it becomes more manageable for storage and transmission over networks, making it easier and faster to stream to end-users.
Bandwidth Efficiency:
Efficient video encoding techniques help reduce the required bandwidth for streaming videos (read what is bandwidth). This is particularly crucial in scenarios with limited network capacity or when serving many viewers simultaneously. Lower bandwidth requirements result in smoother streaming experiences and reduced buffering, ensuring viewers can enjoy content even with varying internet speeds.
Adaptive Bitrate Streaming:
Video encoding enables adaptive bitrate streaming, a crucial feature for delivering high-quality video across diverse network conditions and devices. Content is encoded at multiple bitrates and resolutions, and during streaming, the player dynamically switches between different versions based on the viewer’s available bandwidth. This ensures uninterrupted playback and the best possible quality for each viewer.
Device Compatibility:
Different devices have varying capabilities, screen sizes, and processing power. Video encoding ensures that content can be played on a wide range of devices, from smartphones and tablets to smart TVs and desktop computers. By supporting various video codecs and resolutions, video streaming platforms can reach a broader audience.
Real-Time Encoding:
For live streaming events, real-time video encoding is essential. It involves encoding the live video feed on-the-fly as the event unfolds and transmitting it to viewers in real-time. This requires specialized hardware and software solutions to maintain low latency and deliver a seamless viewing experience.
Content Security:
Video encoding can also play a role in content protection by enabling Digital Rights Management (DRM) solutions. Encrypted video streams can prevent unauthorized access and distribution of copyrighted content, ensuring that only authorized users can view the videos.
Video Quality Control:
Video encoding allows content creators and distributors to control the quality of their videos. By adjusting the encoding settings, they can strike a balance between file size and visual quality, ensuring that their content looks its best while remaining accessible to viewers with various internet speeds.
What is Progressive Video Encoding?

Progressive Video Encoding is an innovative approach to video compression and delivery that aims to enhance the user experience during video streaming. Unlike traditional video streaming methods that require the entire video to be downloaded before playback can begin, progressive video encoding allows viewers to start watching the video almost immediately, even as the video continues to load in the background.
The key concept behind progressive video encoding is the creation of a video file that contains multiple layers of increasing quality and detail. When a user initiates video playback, the player can quickly access the lower quality layers, allowing for rapid display of the initial frames. As the video continues to load, the player seamlessly switches to higher quality layers, progressively improving the visual quality of the playback.
What is Interlaced Video Encoding?
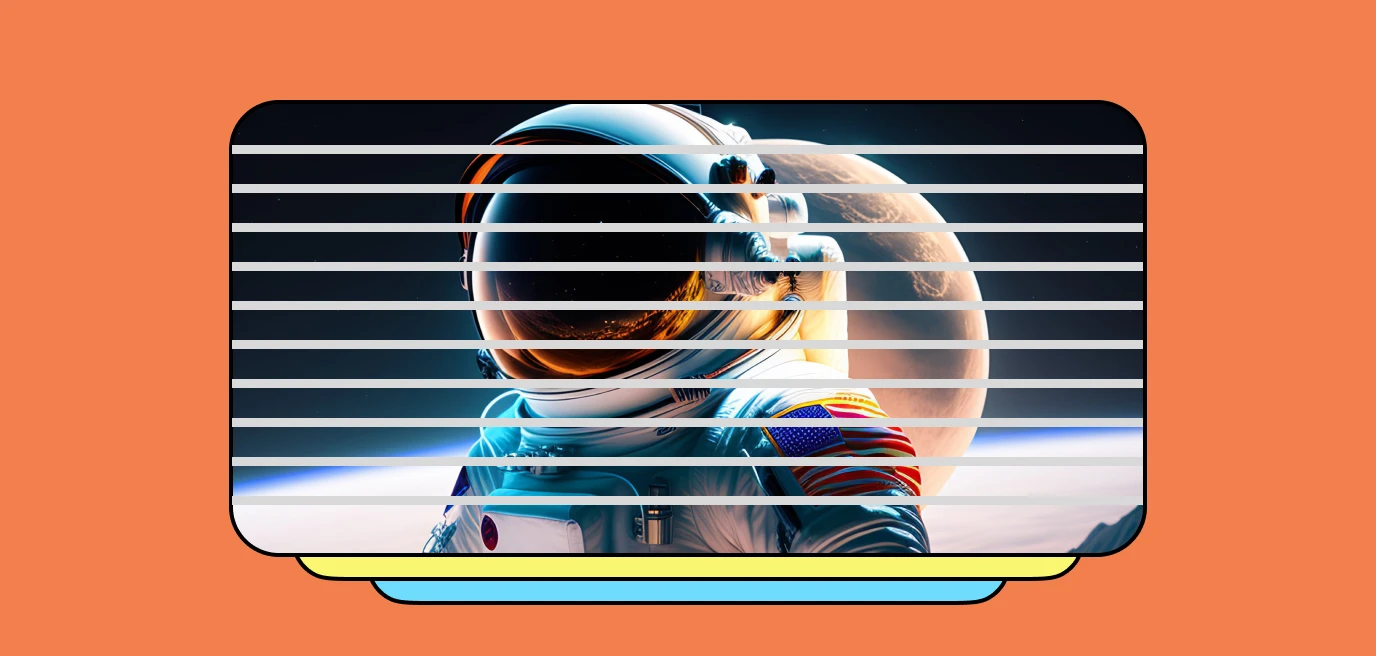

Interlaced video encoding is a traditional method of video compression that was widely used in analog television broadcasting and early digital video formats. It is an older technique that has largely been replaced by progressive video encoding in modern video systems. However, it is essential to understand interlaced video encoding as it was prevalent in the past and is still encountered in certain legacy systems and content.
In interlaced video encoding, each video frame is divided into two separate fields, referred to as odd and even fields. The odd field contains the lines of the video frame with odd-numbered horizontal positions, while the even field contains the lines with even-numbered horizontal positions. These fields are captured and displayed sequentially, creating a perceived full frame.
What are the Technical Aspects of Progressive Video Encoding?
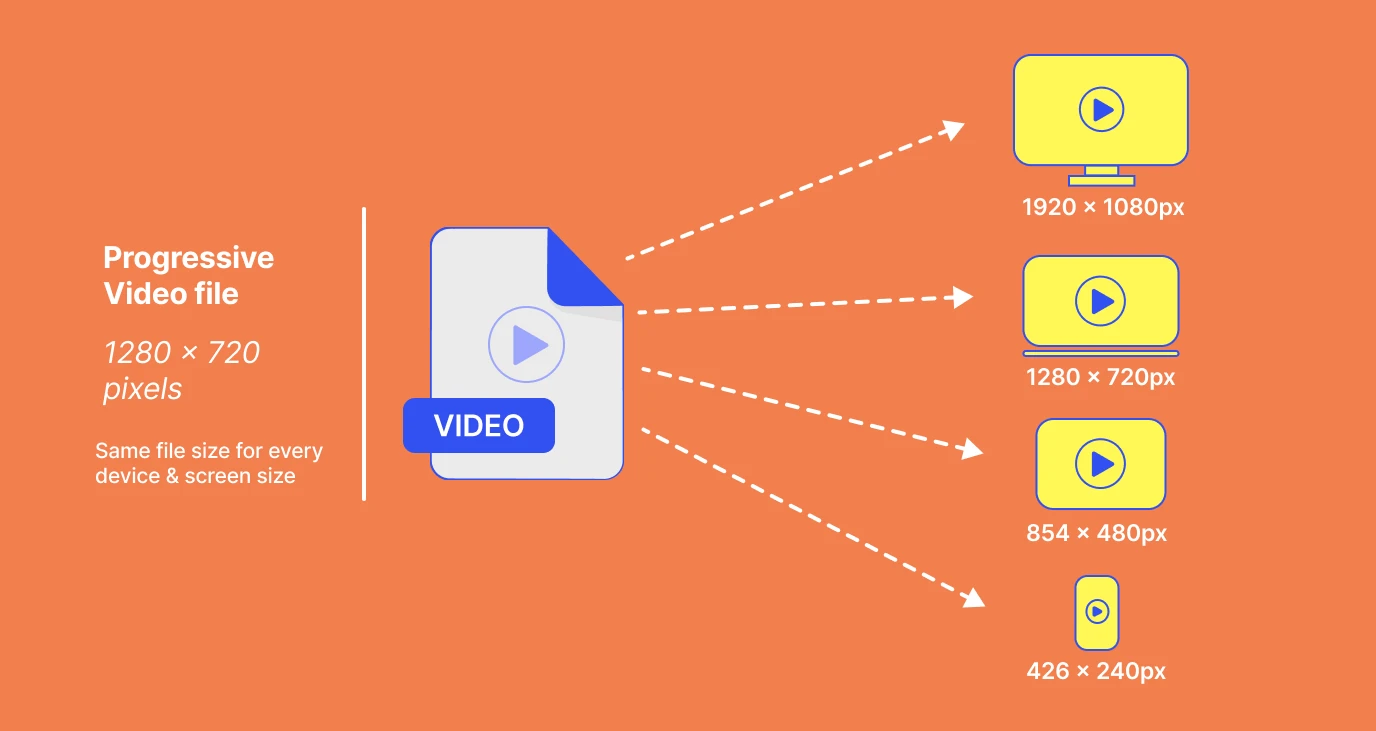
Progressive Video Encoding involves several technical aspects to achieve its goal of delivering smooth and efficient video streaming. Here are the key technical aspects of progressive video encoding:
Multi-Bitrate Encoding:
Progressive video encoding typically involves creating multiple versions of the same video at different bitrates and resolutions. These different renditions allow adaptive bitrate streaming, where the player can dynamically switch between versions based on the viewer’s internet connection speed and device capabilities.
Codec Selection:
Selecting the appropriate video codec is crucial in progressive video encoding. Modern video codecs like H.264, H.265 (HEVC), VP9, and AV1 are commonly used due to their efficient compression algorithms, which help reduce file size while maintaining visual quality.
GOP (Group of Pictures) Structure:
The choice of Group of Pictures structure impacts video quality and delivery. In progressive encoding, an open-GOP structure is often used to allow for faster start times and better seek ability in the video stream.
Keyframe Placement:
Keyframes, also known as I-frames, are complete frames that can be decoded without reference to other frames. Proper keyframe placement is important for achieving efficient seeking within the video and for enabling fast start times during playback.
Adaptive Streaming:
To enable adaptive bitrate streaming, the video server needs to support protocols like Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP (DASH) or HTTP Live Streaming (HLS). These protocols allow the player to choose the appropriate bitrate version of the video based on real-time network conditions.
Buffering and Preloading:
To ensure smooth playback, the video player needs to buffer and preload enough video data. This is done to handle fluctuations in network bandwidth and maintain a consistent viewing experience without frequent buffering interruptions.
Metadata for Adaptive Streaming:
To facilitate adaptive streaming, metadata is often included in the video file or provided through separate manifest files. This metadata provides information about the available bitrates, resolutions, and segment durations, which helps the player make informed decisions during streaming.
Streaming Protocols:
The choice of streaming protocol, such as MPEG-DASH, HLS, or Smooth Streaming, can impact how the video data is delivered to the player. Different protocols have varying support for adaptive streaming and features like server-side ad insertion.
Transcoding:
To support a wide range of devices and platforms, video files may need to be transcoded into different formats, resolutions, and bitrates. This transcoding process is essential for ensuring compatibility across various devices.
Latency Considerations:
In real-time applications like live streaming, minimizing latency is critical. Progressive video encoding must consider low-latency encoding settings to ensure that the content reaches the viewer as quickly as possible.
Advantages of Progressive Video Encoding
Progressive Video Encoding offers several advantages that contribute to an overall enhanced video streaming experience. Let’s delve into each of these advantages:
Improved User Experience:
Progressive video encoding significantly reduces buffering and start times, allowing viewers to begin watching the video almost immediately. This seamless playback experience eliminates frustrating delays, leading to higher viewer satisfaction and engagement.
Better Video Quality:
By providing multiple quality layers, progressive video encoding ensures that viewers get the best possible video quality based on their internet connection and device capabilities. As the video progressively loads, the player seamlessly switches to higher quality layers, resulting in a visually pleasing and uninterrupted viewing experience.
Enhanced Compatibility:
Progressive video encoding is compatible with a wide range of devices and platforms. It can be played on smartphones, tablets, desktop computers, smart TVs, and other connected devices, making it a versatile solution for content distribution.
Bandwidth Efficiency:
Adaptive bitrate streaming, made possible by progressive video encoding, optimizes bandwidth usage. The video player can adjust the quality on-the-fly, ensuring that viewers with varying internet speeds can watch the content without buffering or sacrificing quality.
Streaming Performance:
With progressive video encoding, streaming performance is improved as the video starts playing almost immediately. This is especially valuable for live events and time-sensitive content, where viewers expect real-time access to the video stream.
Still Frame Quality:
Even in scenarios with limited bandwidth, progressive video encoding ensures that still frames are of acceptable quality. This means that even if the connection fluctuates during playback, viewers can still see clear and detailed images without significant pixelation.
Viewing Experience:
The combination of reduced buffering, smooth playback, and adaptive quality results in an overall superior viewing experience. Viewers can enjoy the content without interruptions or compromises in video quality, making their streaming sessions more enjoyable.
Reduction in Encoding Time
In progressive video encoding, the video is divided into multiple quality layers, and the lower-quality layers are encoded first. These layers are often quicker to encode as they contain less detailed information. Encoding time is substantially reduced, resulting in an impressive decrease of 50-60%.
Progressive Video Encoding with Muvi One
At Muvi, we take video seriously and that is why we have introduced Progressive Video Encoding for faster and more efficient video encoding. This innovative feature offers remarkable advantages to users, most notably a noteworthy 50-60% reduction in encoding time. By prioritizing the delivery of the low-quality output first, it rapidly prepares the content for seamless streaming. Subsequently, high-quality outputs are seamlessly delivered. Hence users can enjoy faster access to content, resulting in an enhanced overall experience characterized by uninterrupted and seamless streaming.
Muvi One’s progressive encoding feature enables your end-users to play the content as soon as the first encoded version is available, the feature improves the overall user experience. Instead of waiting for the entire video to encode, users can start streaming and watching the content immediately, resulting in a seamless and uninterrupted viewing experience. Start a free trial to explore amazing features of Muvi One!
FAQs
What is Progressive Video Encoding?
Progressive Video Encoding is an innovative approach to video compression and delivery that aims to enhance the user experience during video streaming. Unlike traditional video streaming methods that require the entire video to be downloaded before playback can begin, progressive video encoding allows viewers to start watching the video almost immediately, even as the video continues to load in the background.
How does Progressive Video Encoding differ from Interlaced Encoding?
Progressive Video Encoding and Interlaced Encoding are two different approaches to representing and transmitting video images. In progressive video encoding, each frame of the video is displayed in a complete and sequential manner. The entire frame is encoded and displayed from top to bottom in one go. Interlaced encoding was more common in older video systems and CRT (cathode ray tube) displays. In this method, each frame is divided into two fields: odd and even lines.
What is the main goal of Progressive Video Encoding?
Progressive video encoding significantly reduces buffering and start times, allowing viewers to begin watching the video almost immediately. This seamless playback experience eliminates frustrating delays, leading to higher viewer satisfaction and engagement. Progressive video encoding is compatible with a wide range of devices and platforms. It can be played on smartphones, tablets, desktop computers, smart TVs, and other connected devices, making it a versatile solution for content distribution.
How does Progressive Video Encoding enhance visual quality?
Progressive Video Encoding enhances visual quality by presenting each frame of a video in a complete and sequential manner, which offers several benefits over other methods like interlaced encoding.
Which is better progressive or interlaced video encoding?
Progressive and interlaced video encoding are two different methods of displaying video content. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages, and which one is “better” depends on the specific context and use case. Progressive video displays all the lines of a frame in sequential order, from top to bottom. Each frame is a complete image, and there is no splitting of the frame into odd and even lines as in interlaced video. While, interlaced video displays frames by splitting them into two fields: odd and even lines. In each field, only half of the lines are displayed at a time, alternating between odd and even lines.
What is progressive video format?
Progressive video format refers to a method of displaying and encoding video content in a way that each frame is presented sequentially, with all lines of the frame displayed at once. In other words, each frame consists of a complete image, providing smooth and continuous motion.
What is difference between interlaced and progressive video?
Interlaced and progressive video are two different methods of displaying and encoding video content. They differ in how they present the images on the screen and how the frames are captured, transmitted, and displayed.
Is 4K progressive or interlaced?
4K resolution is typically used in a progressive format, not in an interlaced format. 4K refers to a resolution of approximately 3840×2160 pixels for consumer displays, and it’s commonly denoted as “4K UHD” (Ultra High Definition). This resolution provides a higher level of detail and clarity compared to lower resolutions.






















Add your comment