Streaming in UHD or 4K is the new norm. But do you know a 2-hour long 4K video would hog over 1.8 TB of storage when uncompressed and streamed?
So, how do video streaming platforms like Netflix, Prime Video, and YouTube manage to store and stream such large video files, that too in huge volumes? How much are their storage and bandwidth costs?
The big names in the video streaming space use modern video compression technology (Codecs) to reduce file size while keeping video quality optimal for seamless delivery across devices. But how?
They use the best video codecs ever made, i.e., AV1, H265 (HEVC), and VP9.
∴Fact you must know
“Streaming and Chilling would never have been coined together without the invention of video codecs. It’s like, codecs are the reason, viewers comfortably stream their favorite videos even with limited bandwidth.”
At Muvi, we have mastered the art of super-fast yet efficient video encoding. Our video compression technology supports popular video codecs like AVC, HEVC, VP9, and AV1. Encoding videos with Muvi is fast, easy, simple, code-free, and, most importantly, affordable. Deliver lag-free video playback up to 4K resolution, keeping your storage and bandwidth costs at a minimum.
Sign up to take a free trial. No credit card required, cancel anytime.
What is a Video Codec?
A video codec is a ready-made software algorithm used for compressing and decompressing video streams. The modern compression techniques compress high-definition videos into a more manageable size, ensuring seamless content storage as well as delivery.
The best thing about using a video codec is that there is no compromise in the video quality during the compression and decompression process. It’s simple, codecs are in charge of interpreting all the data and content stored in the video files and controlling how the video is streamed on the user’s screen.

How do Video Codecs Work?
The best video codecs work on multiple compression algorithms, such as chroma subsampling and motion compression. The video compression works in three simple steps:
- Identify the patterns or elements in the video that can be removed
- Clear out all the unnecessary information from the video that is invisible to viewers
- Quickly compress the remaining data and convert the video into a streamable size.
Video Codecs are mainly categorized into two types – lossless and Lossy. The lossless video codecs preserve all the data and information during video compression, while the lossy video codecs prioritize higher compression ratios by removing redundant video frame data such as intra-frame and inter-frame information.
Role of Video Codec in Streaming
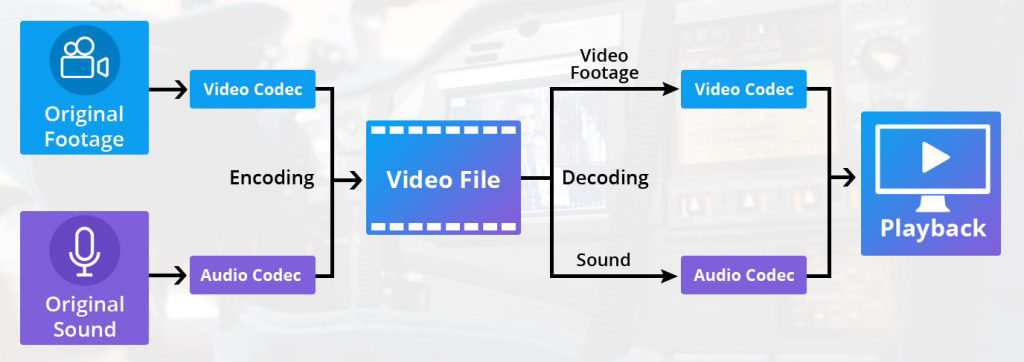
- At the core, codecs are advanced video compression tools that work on encoding and decoding algorithms. In order to deliver uninterrupted video streams on user’s screen, codecs eliminate out certain un-necessary data from the videos and reduce the file size without hampering its overall quality.
- Once compressed, all the components of the video are wrapped into a specific file format, termed as Containers. Generally, the containers store video codecs, audio codecs, closed captioning, and other important metadata, supporting multiple file formats such as MKV, MP4, WMV, AVI, MOV, QT, and AVCHD.
∴Fact you must know
“When a file streams at thirty-frames per second (high-quality video file), the requirement for storage space and bandwidth balloons quickly. If the streaming platform, delivering the video, fails to meet the requirements, then there are high chances, the end-users will experience trouble in watching the videos online.”
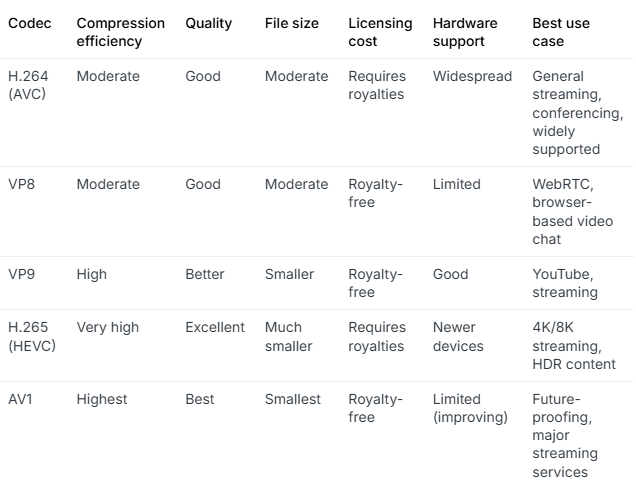
Comparing the Best Video Codecs for Streaming in 2026

Now, though you are clear about what is a video codec and how it works, let’s have a look at the most popular video codecs in the OTT space and compare AV1 vs H.265 vs VP9.
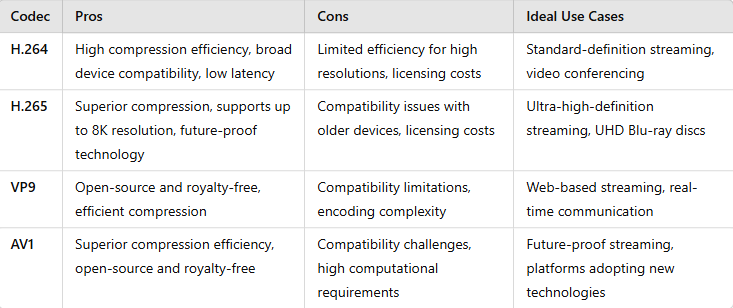
H.264/AVC – Best Video Codec For Low-Latency Streaming

H.264 or AVC (Advanced Video Coding) is a widely supported legacy video codec that enables playback on both outdated and new devices. Because of its motion-compensation-based video compression standards, AVC is highly recommended for recording, compression, and streaming of video files across multiple devices including Laptops, Mobile Phones, Desktops, Tablets, Smart TVs, and gaming consoles.
Apart from streaming market, H.264 holds a significant penetration in Cable Broadcasting and Blu-Ray disk distributions. Mostly, AVC is combined with AAC audio codec and is stored in 3GP, MOV, F4V, TS, and MP4 Containers.
The most exciting benefit of integrating H.264 is the distribution of 50% smaller files as compared to previous generation codecs – MPEG-2 and H.263.
- Platform Compatibility: H.264 has gained widespread support across various devices, including smartphones, tablets, computers, smart TVs, and streaming devices. AVC is also supported across popular CDNs and web browsers.
- Low Latency: H.264 allows for relatively low latency in real-time applications, such as video conferencing and live streaming.
- Decoding Protocols: Many modern devices have hardware decoding support for H.264/AVC, which offloads the decoding process from the CPU, resulting in improved energy efficiency and reduced power consumption during video playback.
- System Requirements For Encoding: A dual core CPU with a minimum of 2.0 GHz processor speed. RAM requirements would be at least 1GB for 1080p 30 FPS videos and 2 GB for 4K 60 FPS videos.
- AVC Usage Cost: Licensing process of AVC is handled by MPEG LA. The royalty on AVC usage is charged on a subscription basis ranging from $25,000 to $100,000. No royalty is charged if the no. of subscriptions is below 100,000.
H.265/HEVC – Best Video Codec For High-Definition Streaming

H.265 or HEVC (High-Efficiency Video Coding) is termed as the spiritual successor of AVC. It delivers 25% to 50% better compression efficiency with improved or same-level of video quality. Similar to AVC, it supports 8K UHD resolution, but comparatively delivers smaller files that require low bandwidth for streaming.
Considering the content-capturing systems in next-generation HDTV displays, HEVC is designed with advanced video coding layers, parallel processing tools, motion vector predictions, and other essential coding extensions.
Presently, H.265/HEVC video codec is competing with the open-sourced and royalty-free AV1 coding format and it’s Main10 profile has been incorporated into nearly all supporting hardware.
- Support for Higher Resolutions: H.265/HEVC supports higher resolutions, including 4K and even 8K, which is particularly important as higher-resolution content becomes more prevalent in the market.
- Better Handling of High-Motion Sequences: H.265/HEVC excels in handling high-motion sequences, such as sports events or action scenes, by efficiently compressing complex motion without compromising the quality.
- Reduced Bandwidth Consumption: The improved compression efficiency of H.265/HEVC results in reduced bandwidth consumption, making it cost-effective for video streaming and other bandwidth-sensitive applications.
- Support for Parallel Processing: H.265/HEVC supports parallel processing, which allows for faster video encoding and decoding, making it more suitable for real-time applications and video processing in modern devices.
- HEVC Usage Cost: HEVC/H.265 patent licensing is managed by both MPEG-LA and Access Advance (HEVC Advance). The royalty on HEVC usage is charged per subscriber, i.e. $0.025 USD per subscriber.
Comparing, AVC vs HEVC or H.264 vs H.265, which video codec is better for streaming? H.264/AVC may not compress high resolution videos in 4K or 8K as efficiently as HEVC would.
VP9 – Best Video Codec For Web-based Streaming

VP9 is a royalty-free alternative to HEVC, developed by Google. Every chrome browser, Android phones, and even Google’s own video streaming platform YouTube, supports VP9 for seamless delivery of videos to end-users.
The codec offers better video quality at the same bit rate as HEVC and thus is highly effective for delivering 4K HD videos online. As the efficiency and performance of VP9 are pretty similar to AV1, it is often termed as AV0 (an earlier version of AV1).
- Hardware Efficiency: Many modern devices and processors come with hardware acceleration support for VP9, which reduces the computational burden on software-based decoding, leading to smoother video playback and reduced power consumption on such devices.
- Adaptive Bitrate Streaming: VP9 supports adaptive bitrate streaming, which enables seamless switching between different video quality levels based on the user’s internet connection speed, ensuring an uninterrupted viewing experience.
- Flexible Encoding Profiles: VP9 offers multiple encoding profiles, including 4:2:0, 4:2:2, and 4:4:4 chroma subsampling, allowing content creators to choose the right profile based on their specific needs.
- Platform Compatibility: VP9 is well-supported across devices, OS, CDNs, and browsers. It’s supported by Windows, macOS, Linux, like the most-used operating systems. Also, browsers like Chrome, Safari, Firefox support the VP9 codec. Except Microsoft Edge.
- VP9 Usage Cost: There is no usage cost for VP9 codec. It is offered royalty-free by Google.
Comparing HEVC vs VP9, which video codec is best for streaming? HEVC is not royalty-free, but VP9 is royalty-free. This is the main difference between HEVC and VP9 codec.
And comparing VP9 vs AVC, VP9 offers much efficient compression than AVC, making it suitable for ultra-high definition streaming.
AV1 – Best Video Codec For Future-Proof Streaming

AV1 is truly the Ultimate video coding format developed by Alliance for Open Media (AOM), along with the support of Google, Amazon, Cisco, Microsoft, Mozilla, and Netflix. It is an open, royalty-free video codec, which is specifically designed to improve the encoding and decoding efficiency by 30% over HEVC’s performance.
Because of its low computational footprints and quick hardware optimization abilities, AV1 delivers highest-quality real-time videos, scalable to any modern device at any bandwidth.
The algorithms used in AV1 are quite more advanced than HEVC. This newer codec is intended for use in WebRTC and HTML5 Web Video together with Opus audio codec format.
- Royalty-Free and Open Source: AV1 is a royalty-free and open-source video codec, meaning that anyone can use it without incurring licensing fees. This aspect promotes broader adoption and ensures that content creators and developers can freely implement and distribute AV1 in their projects
- Industry Support: AV1 has garnered support from major technology companies, including Google, Amazon, Microsoft, Apple, Netflix, and more. This support ensures the availability of hardware and software implementations, fostering its adoption across various platforms and devices.
- Scalability: AV1 is designed to be scalable, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, from mobile devices to high-end professional video production. It can efficiently handle resolutions from SD (Standard Definition) to 4K and beyond.
- Support for HDR and WCG: AV1 includes native support for High Dynamic Range (HDR) and Wide Color Gamut (WCG), allowing for enhanced visual experiences with more vibrant colors and a broader range of brightness levels.
- Efficient Parallel Processing: AV1 takes advantage of modern hardware capabilities, including multi-core CPUs and GPUs, to enable faster video encoding and decoding through parallel processing.
Comparing AV1 vs HEVC and AVC, AV1 offers up to 50% better compression than H.264 and H.265, making it highly efficient for streaming, and AV1 is also royalty-free, hence, there will be less streaming expenses.
But comparing AV1 vs VP9, where both are royalty-free for usage, AV1 offers 30% more compression efficiency than VP9 but the high computational requirements for encoding and decoding AV1 are challenging to maintain.
VVC – The Upcoming Standards of Video Codec

Versatile Video Coding (VVC), also known as H.266 or MPEG-I Part 3, is a video compression standard that is developed to succeed the widely used High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC or H.265).
VVC is developed by the Joint Video Experts Team (JVET), a collaborative effort between the ITU-T Video Coding Experts Group (VCEG) and the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG).
The main objective of VVC is to provide significantly improved compression efficiency over its predecessors, allowing for higher quality video at lower bitrates.
- Support for Emerging Technologies: VVC is designed to accommodate modern video technologies such as high dynamic range (HDR) and 360-degree videos. This is essential for delivering immersive and visually stunning experiences to users across various platforms.
- Increased Bit Depth: VVC supports higher bit depths, which results in more accurate and nuanced color representation. This is particularly beneficial for applications that require precise color grading and reproduction, such as professional video editing and medical imaging.
- Flexibility in Bitrate Allocation: VVC’s improved compression efficiency provides content creators and distributors with more flexibility in allocating bitrates. They can allocate more bits to specific portions of the video that require higher detail and retain quality in less critical areas.
- Industry Standardization: VVC is developed and standardized by recognized industry organizations, such as ITU-T and MPEG. This ensures that VVC is well-supported and widely adopted across various industries and platforms.
If you want to know further about video codecs, you can talk with our experts.
Factors to Consider When Choosing The Best Video Codec
Hope the above comparison of AV1 vs HEVC vs VP9 gave you an overall idea of the most commonly used video codecs in the streaming space. We suggest considering the following critical factors for choosing the best video codec.
- Playback Quality: The codec’s ability to maintain high visual fidelity during compression directly affects the viewer’s experience. Advanced codecs like H.265 (HEVC) and AV1 offer superior compression efficiency, preserving quality even at lower bitrates. However, it’s crucial to balance quality with other considerations, such as compatibility and computational requirements.
- File Size: Efficient compression reduces file sizes, leading to faster load times and reduced buffering. Codecs like H.265 and AV1 provide significant compression advantages over older codecs like H.264, enabling smoother streaming experiences, especially for high-definition content.
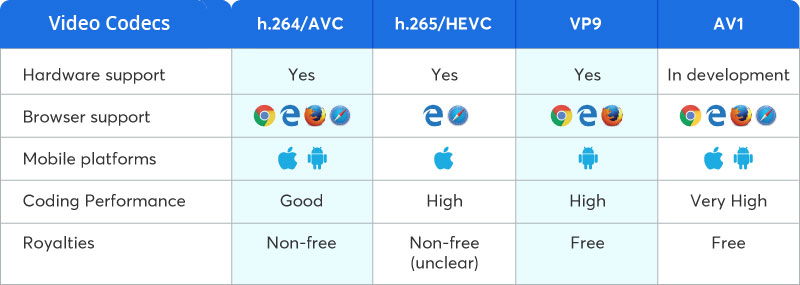
- Ease-of-Integration: The video codec’s compatibility with various devices, platforms, and browsers determines its ease of integration. While H.264 enjoys widespread support, modern video codecs like HEVC, VP9, and AV1 are gaining traction but may still face compatibility challenges.
- Cost: Licensing fees can impact the overall cost of using a particular codec. Open-source and royalty-free codecs like AV1 and VP9 eliminate licensing costs, making them attractive options for budget-conscious streaming services.
Selecting the best video codec for streaming involves balancing playback quality, file size, integration ease, and cost. Understanding these factors enables you to choose a popular video codec that aligns with your streaming goals and audience needs.
Which is the Best Video Codec for Streaming in 2026?
The best video codec ultimately depends on what your streaming needs.
H.264 or AVC is a time-tested video codec that is known for its widespread adoption. older version of the video coding format. But with the introduction of numerous advancements in compression techniques and new video technologies like HDR & VR, it’s for sure, the integration of AVC codec will soon be replaced.
HEVC, the successor of AVC, has been in place for almost over a decade, but still, content distributors are hesitating to adopt its compression standards because of expensive and tedious configurations.
Google’s VP9 is a powerful codec doubtlessly, but it failed to gain widespread adoption because of its complex patent licensing process. Considering VP9’s learned-lessons, Google later decided to support the development of AOM’s royalty-free AV1.
Now talking about the latest video codec – AV1 is exclusively designed to be more performant than all the available codecs in the market. It is an open-sourced codec with hassle-free patent licensing, and the integration manages to save upto 30% of the bandwidth for the same image quality.
The surprising thing, Netflix, Prime Video, and Jio Hotstar are using AV1 codec in their encoding engines and hence are able to deliver seamless high-resolution videos
So, if you are looking for a next-generation performance-oriented video codec that is limited by bandwidth and licensing cost, AV1 is the perfect codec.
Else, you can go with HEVC for its real-time, and low latency encoding process. But remember, as time will pass on, both the streaming industry and technological developments will ultimately shift towards AV1 and its successors.
At Muvi, we definitely believe that AV1 will have a positive impact on the streaming industry in the next five years. Considering that, we offer a fully managed, built-in streaming engine for multi-codec video delivery.
Ready to get started with High-Definition uncompromised video streaming journey with Muvi? Click here to sign up.

Related Blogs to Video Codecs:
H264 vs H265: Which Video Codec is Better?
VP9 vs AV1: Which Video Codec Offers Superior Performance
Decoding the VVC Codec
Exploring Low Latency 4K Streaming through VVC
High-Efficiency Video Codec (HEVC Video): All You Need to Know
Decoding the VP9 Codec























Add your comment