The importance of video cloud streaming has become more evident than ever before. As we step into 2025, online video content continues to expand, offering both challenges and opportunities for content creators, businesses, and consumers alike.
According to a report by Statista, The Video Streaming (SVoD) market is poised to achieve significant milestones, with expected revenues reaching US$108.50 billion worldwide by 2025, showcasing a robust growth trajectory. Projections suggest a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 8.27% from 2025 to 2027, propelling market volume to US$137.70 billion by 2027. These forecasts underscore the promising potential and expanding opportunities within the industry.
What Is Video Cloud Streaming?
Video cloud streaming refers to the process of delivering video content over the internet using cloud-based infrastructure. Instead of hosting video files on local servers, video cloud streaming services utilize cloud servers to store, manage, and deliver video content to viewers across various devices.
How Does Cloud-based Video Streaming Work?
Content Ingestion:
Video content is uploaded to the cloud infrastructure. This can include live video feeds or pre-recorded video files.
Encoding and Transcoding:
Once the content is uploaded, it undergoes encoding and transcoding processes. Encoding involves compressing the video files into various formats and bitrates suitable for different devices and internet connection speeds. Transcoding is the process of converting video files into different resolutions and formats to optimize playback across different devices and bandwidth conditions.
Storage:
The encoded and transcoded video files are stored in the cloud storage infrastructure. Cloud storage provides scalability and flexibility, allowing video streaming platforms to store large volumes of video content securely.
Content Delivery Network (CDN):
To ensure fast and reliable delivery of video content to viewers worldwide, video cloud streaming services typically utilize content delivery networks (CDNs). CDNs consist of a network of servers distributed across different geographical locations. When a viewer requests to watch a video, the CDN delivers the content from the nearest server, reducing latency and improving streaming performance.
Adaptive Bitrate Streaming:
Video cloud streaming platforms often employ adaptive bitrate streaming techniques. This allows the video player to dynamically adjust the bitrate and resolution of the video stream based on the viewer’s internet connection speed and device capabilities. Adaptive bitrate streaming helps to deliver a smooth and uninterrupted viewing experience, even in fluctuating network conditions.
Analytics and Monetization:
Video cloud streaming services offer analytics tools to track viewer engagement, analyze viewing patterns, and gain insights into audience behavior. Additionally, many platforms support monetization features such as advertising, subscription models, pay-per-view, or digital rights management (DRM) to generate revenue from video content.
The Benefits of Video Cloud Streaming
Scalability:
Video cloud streaming platforms offer scalability, allowing businesses to easily accommodate fluctuations in viewer demand without the need for significant infrastructure investments. Whether a video attracts a handful of viewers or experiences a sudden surge in traffic, cloud-based solutions can dynamically scale resources to ensure smooth streaming experiences for users.
Global Reach:
Cloud streaming enables content delivery to audiences worldwide, leveraging the global network infrastructure of cloud service providers. This ensures that viewers from different geographic locations can access video content with minimal latency and buffering, thereby enhancing user experience and expanding the reach of content creators.
Top CDN (Content Delivery Network):
Utilizing a top CDN ensures optimized content delivery by caching video files in servers distributed across various geographical locations. This reduces latency and accelerates content loading times, regardless of where viewers are located.
Cost-Effectiveness:
Cloud streaming platforms typically operate on a pay-as-you-go model, allowing businesses to avoid upfront infrastructure costs and only pay for the resources they consume. This cost-effective approach enables startups and small-scale content creators to enter the video streaming market without significant financial barriers.
Flexibility:
Video cloud streaming solutions offer flexibility in terms of customization and integration with existing workflows and applications. They support various video formats, codecs, and streaming protocols, enabling businesses to deliver content across multiple devices and platforms seamlessly.
Analytics and Insights:
Cloud streaming platforms provide robust analytics and reporting tools that offer insights into viewer behavior, engagement metrics, and performance analytics. This data enables content creators to make informed decisions regarding content optimization, audience targeting, and monetization strategies.
Security:
Security is a paramount concern for video content, especially when dealing with sensitive or proprietary information. Cloud streaming platforms employ advanced security measures such as encryption, access controls, and digital rights management (DRM) to protect content against unauthorized access, piracy, and data breaches.
Monetization Opportunities:
Video cloud streaming platforms offer various monetization models, including subscription-based services, pay-per-view, advertising, and sponsorship opportunities. This enables content creators to generate revenue from their video content through diverse channels and business models.
Content Management:
Cloud streaming platforms provide comprehensive content management capabilities, including asset management, metadata tagging, content indexing, and version control. This streamlines the content creation and publishing workflow, enabling efficient management of large video libraries and archives.
Reliability and Redundancy:
Cloud streaming platforms leverage redundant architectures and failover mechanisms to ensure high availability and reliability. By distributing content across multiple servers and data centers, they minimize the risk of downtime and service interruptions, thereby ensuring uninterrupted streaming experiences for viewers.

Features To Look For in Cloud Video Streaming Platform
Cloud Hosting:
A video streaming platform should offer cloud hosting capabilities, meaning it stores your video content on remote servers accessible via the Internet. Cloud hosting provides scalability, reliability, and accessibility, allowing users to stream videos from anywhere with an internet connection. It also eliminates the need for on-premises infrastructure, reducing costs and maintenance efforts.
Video CMS (Content Management System):
A robust video CMS is essential for organizing, managing, and delivering your video content effectively. It should provide features such as content categorization, metadata management, search functionality, scheduling tools, and version control. A user-friendly interface is crucial to simplify content uploading, editing, and distribution tasks.
Built-in CDN (Content Delivery Network):
A CDN optimizes the delivery of video content by distributing it across multiple servers strategically located around the world. This reduces latency, ensures faster load times, and enhances the streaming experience for users regardless of their geographical location. A built-in CDN also helps handle spikes in traffic and improves overall reliability and scalability.
Analytics:
Analytics tools are essential for gaining insights into viewer behavior, engagement metrics, and the performance of your video content. Key analytics features include viewer demographics, playback statistics, engagement metrics (e.g., watch time, drop-off points), device and platform data, and conversion tracking. These insights help optimize content strategies, improve user experience, and maximize monetization opportunities.
Multi-DRM Security:
Digital Rights Management (DRM) ensures that your video content is protected against unauthorized access, piracy, and distribution. A multi-DRM solution supports various DRM technologies (e.g., Widevine, FairPlay, PlayReady) to encrypt and securely deliver content across different devices and platforms while enforcing access controls and license management.
Geo-blocking:
Geo-blocking allows you to restrict access to your video content based on the viewer’s geographical location. This feature is crucial for complying with content licensing agreements, regional copyright laws, and content distribution rights. Geo-blocking helps prevent unauthorized access from regions where your content is not licensed or legally available.
Multiple Monetization Models:
A cloud video streaming platform should support various monetization models to help you generate revenue from your video content. This includes subscription-based models, pay-per-view (PPV), advertising (pre-roll, mid-roll, post-roll), sponsorship, premium content offerings, and transactional models. Flexibility in monetization options enables you to tailor your revenue strategy to your audience and content niche.
HTML5 Online Video Player:
An HTML5 online video player offers compatibility with a wide range of devices, browsers, and operating systems without requiring additional plugins or software installations. It should provide features such as adaptive bitrate streaming, customizable player controls, full screen mode, captions/subtitles support, and seamless integration with your branding and user interface design.
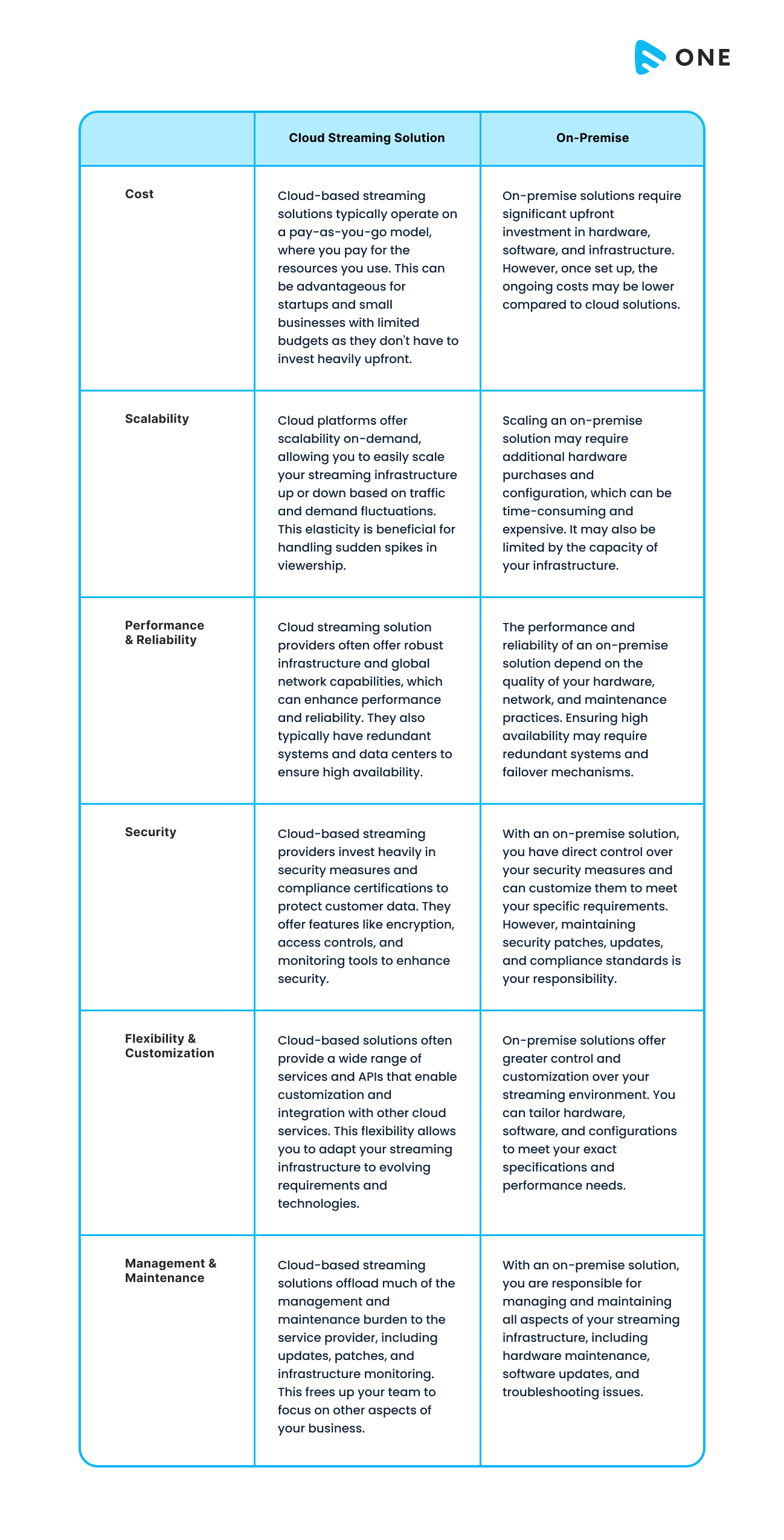
Video Streaming On Cloud VS On-Premise: 6 Considerations
Ending Notes
Muvi One is a comprehensive cloud-based video streaming solution that helps your video streaming service instantly. With multiple monetization models, Muvi One helps you monetize your video content and generate revenue seamlessly. Our no-code setup helps you launch OTT apps across 16+ ecosystems. Start your free trial and we will help you on your journey to video streaming success.


















Add your comment